Stereotactic body radiation therapy as an alternative treatment for small hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 24255719
- PMCID: PMC3821847
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079854
Stereotactic body radiation therapy as an alternative treatment for small hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Even with early stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), patients are often ineligible for surgical resection, transplantation, or local ablation due to advanced cirrhosis, donor shortage, or difficult location. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) has been established as a standard treatment option for patients with stage I lung cancer, who are not eligible for surgery, and may be a promising alternative treatment for patients with small HCC who are not eligible for curative treatment.
Materials and methods: A registry database of 93 patients who were treated with SBRT for HCC between 2007 and 2009 was analyzed. A dose of 10-20 Gy per fraction was given over 3-4 consecutive days, resulting in a total dose of 30-60 Gy. The tumor response was determined using dynamic computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, which was performed 3 months after completion of SBRT.
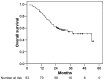
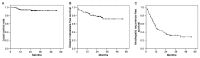
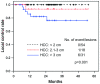
Results: The median follow-up period was 25.6 months. Median size of tumors was 2 cm (range: 1-6 cm). Overall patients' survival rates at 1 and 3 years were 86.0% and 53.8%, respectively. Complete and partial tumor response were achieved in 15.5% and 45.7% of patients, respectively. Local recurrence-free survival rate was 92.1% at 3 years. Most local failures were found in patients with HCCs > 3 cm, and local control rate at 3 years was 76.3% in patients with HCC > 3 cm, 93.3% in patients with tumors between 2.1-3 cm, and 100% in patients with tumors ≤ 2 cm, respectively. Out-of-field intrahepatic recurrence-free survival rates at 1 and 3 years were 51.9% and 32.4%, respectively. Grade ≥ 3 hepatic toxicity was observed in 6 (6.5%).
Conclusions: SBRT was effective in local control of small HCC. SBRT may be a promising alternative treatment for patients with small HCC which is unsuitable for other curative therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

