Lentivirus vector-mediated Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor 2 overexpression induces beta-2 adrenergic receptor desensitization in airway smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 24255780
- PMCID: PMC3815716
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.10.07
Lentivirus vector-mediated Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor 2 overexpression induces beta-2 adrenergic receptor desensitization in airway smooth muscle cells
Abstract
Background: Beta-2 adrenergic receptor (β2AR) downregulation is critical to asthma rescue therapy; however, tolerance, also known as β2AR or bronchodilator desensitization, mechanisms potentially resulting in life-threatening rescue treatment failure remain poorly understood.
Methods: Airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs) from BALB/c mice were primarily cultured. The full-length Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor 2 (RhoGDI2) gene from ASMCs was amplified by RT-PCR, and RhoGDI2 gene was subcloned into the digested PWPXL plasmid. The recombinant lentivirus PWPXL-RhoGDI2 expression plasmid was packaged into mature lentivirus by 293T cells and used to infect ASMCs. Fluorescent quantitation RT-PCR and Western Blot were used to detect the level of mRNA and protein expression of RhoGDI2, β2AR, guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) in overexpression RhoGDI2-ASMCs group, negative GFP control ASMCs group and normal control ASMCs group. Membrane receptor numbers of β2AR was observed by radioligand receptor binding assay in overexpression RhoGDI2-ASMCs group, negative GFP control ASMCs group and normal control ASMCs group.
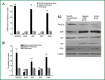
Results: RhoGDI2 vector successfully transfected ASMCs, with infection efficiency (the percentage of GFP-positive cells) >80%. RhoGDI2, GEF and G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) expressions significantly increased in the RhoGDI2 overexpression group compared to control and negative control groups (all P<0.05). Conversely, β2AR and GAP expressions were significantly lower in the RhoGDI2 overexpression group (both P<0.05), exhibiting an inverse correlation with RhoGDI2 expression. Control and negative control groups exhibiting β2AR density more than 2-fold higher than that observed in the RhoGDI2 overexpression group.
Conclusions: RhoGDI2 reduces β2AR density, potentially by reducing β2AR and GAP expressions and increase GEF and GRK2 expressions. Thus, RhoGDI2 is central in cellular β2AR desensitization, though this full mechanism and intermediates merit further investigation.
Keywords: Beta-2 adrenergic receptor (β2AR); G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2); GTPase-activating protein (GAP); Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor 2 (RhoGDI2); desensitization; guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lentivirus vector-mediated Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor 2 induces beta-2 adrenergic receptor desensitization in β2AR desensitization mice model.J Thorac Dis. 2014 Feb;6(2):118-25. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.12.49. J Thorac Dis. 2014. PMID: 24605225 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a cell model of β2-adrenoceptor downregulation.J Thorac Dis. 2013 Aug;5(4):492-7. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.08.32. J Thorac Dis. 2013. PMID: 23991307 Free PMC article.
-
Infant RSV infection desensitizes β2-adrenergic receptor via CXCL11-CXCR7 signaling in airway smooth muscle.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 15:2025.01.13.632772. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.13.632772. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39868223 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The Dual Function of RhoGDI2 in Immunity and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):4015. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044015. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The faces and friends of RhoGDI2.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012 Dec;31(3-4):519-28. doi: 10.1007/s10555-012-9376-6. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012. PMID: 22718398 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Litonjua AA. The significance of beta2-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms in asthma. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2006;12:12-7 - PubMed
-
- Jockers R, Angers S, Da Silva A, et al. Beta(2)-adrenergic receptor down-regulation. Evidence for a pathway that does not require endocytosis. J Biol Chem 1999;274:28900-8 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
