Quantitative methods for evaluating the efficacy of thalamic deep brain stimulation in patients with essential tremor
- PMID: 24255800
- PMCID: PMC3822146
- DOI: 10.7916/D8VM4B0N
Quantitative methods for evaluating the efficacy of thalamic deep brain stimulation in patients with essential tremor
Abstract
Background: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the thalamus is a safe and efficient method for treatment of disabling tremor in patient with essential tremor (ET). However, successful tremor suppression after surgery requires careful selection of stimulus parameters. Our aim was to examine the possible use of certain quantitative methods for evaluating the efficacy of thalamic DBS in ET patients in clinical practice, and to compare these methods with traditional clinical tests.
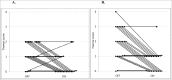
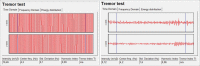
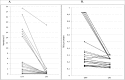
Methods: We examined 22 patients using the Essential Tremor Rating Scale (ETRS) and quantitative assessment of tremor with the stimulator both activated and deactivated. We used an accelerometer (CATSYS tremor Pen) for quantitative measurement of postural tremor, and a eurythmokinesimeter (EKM) to evaluate kinetic tremor in a rapid pointing task.
Results: The efficacy of DBS on tremor suppression was prominent irrespective of the method used. The agreement between clinical rating of postural tremor and tremor intensity as measured by the CATSYS tremor pen was relatively high (rs = 0.74). The agreement between kinetic tremor as assessed by the ETRS and the main outcome variable from the EKM test was low (rs = 0.34). The lack of agreement indicates that the EKM test is not comparable with the clinical test.
Discussion: Quantitative methods, such as the CATSYS tremor pen, could be a useful complement to clinical tremor assessment in evaluating the efficacy of DBS in clinical practice. Future studies should evaluate the precision of these methods and long-term impact on tremor suppression, activities of daily living (ADL) function and quality of life.
Keywords: Quantitative methods; essential tremor; thalamic deep brain stimulation; tremor assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

