Primary focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis and soluble factor urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor
- PMID: 24255893
- PMCID: PMC3832866
- DOI: 10.5527/wjn.v2.i4.103
Primary focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis and soluble factor urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor
Abstract
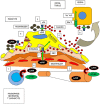
Primary focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) may be due to genetic or acquired etiologies and is a common cause of nephrotic syndrome with high morbidity that often leads to end-stage renal failure. The different available therapeutic approaches are unsuccessful, in part due to partially deciphered heterogeneous and complex pathophysiological mechanisms. Moreover, the term FSGS, even in its primary form, comprises a histological description shared by a number of different causes with completely different molecular pathways of disease. This review focuses on the latest developments regarding the pathophysiology of primary acquired FSGS caused by soluble factor urokinase type plasminogen activator receptor, a circulating permeability factor involved in proteinuria and edema formation, and describes recent advances with potential success in therapy.
Keywords: Plasmin; Podocyte; Primary acquired focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis; Proteinuria; Soluble factor urokinase type plasminogen activator receptor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Proteinuria in Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Apr 16;5:98. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00098. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29713631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A circulating permeability factor in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: the hunt continues.Clin Kidney J. 2015 Dec;8(6):708-15. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfv090. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Clin Kidney J. 2015. PMID: 26613029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Rituximab in Treatment-Resistant Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis With Elevated Soluble Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor and Activation of Podocyte β3 Integrin.Kidney Int Rep. 2021 Oct 30;7(1):68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.10.017. eCollection 2022 Jan. Kidney Int Rep. 2021. PMID: 35005315 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent Primary Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis Managed With Intensified Plasma Exchange and Concomitant Monitoring of Soluble Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor-Mediated Podocyte β3-integrin Activation.Transplantation. 2015 Dec;99(12):2593-7. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000914. Transplantation. 2015. PMID: 26371597 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Urokinase Receptors in Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis: A Review on the Scientific Point of View.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:2068691. doi: 10.1155/2016/2068691. Epub 2016 Jul 18. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27504461 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Podocyturia: Potential applications and current limitations.World J Nephrol. 2017 Sep 6;6(5):221-228. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v6.i5.221. World J Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28948159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble CD40 ligand directly alters glomerular permeability and may act as a circulating permeability factor in FSGS.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 20;12(11):e0188045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188045. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29155846 Free PMC article.
-
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and Scheduled Pretransplant Plasmapheresis: A Timely Diagnosis of Nail-Patella Syndrome Avoided More Futile Immunosuppression.Case Rep Nephrol. 2020 Jul 24;2020:8879555. doi: 10.1155/2020/8879555. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32774956 Free PMC article.
-
Amiloride as an Alternate Adjuvant Antiproteinuric Agent in Fabry Disease: The Potential Roles of Plasmin and uPAR.Case Rep Nephrol. 2014;2014:854521. doi: 10.1155/2014/854521. Epub 2014 May 15. Case Rep Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24959362 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Immune Cells in Hereditary Angioedema.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021 Jun;60(3):369-382. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08842-9. Epub 2021 May 29. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34050913 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benchimol C. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: pathogenesis and treatment. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2003;15:171–180. - PubMed
-
- Korbet SM. Treatment of primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2002;62:2301–2310. - PubMed
-
- Boyer O, Moulder JK, Somers MJ. Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis in children: a longitudinal assessment. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22:1159–1166. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

