Vitamin D-binding protein and vitamin D status of black Americans and white Americans
- PMID: 24256378
- PMCID: PMC4030388
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1306357
Vitamin D-binding protein and vitamin D status of black Americans and white Americans
Abstract
Background: Low levels of total 25-hydroxyvitamin D are common among black Americans. Vitamin D-binding protein has not been considered in the assessment of vitamin D deficiency.
Methods: In the Healthy Aging in Neighborhoods of Diversity across the Life Span cohort of blacks and whites (2085 participants), we measured levels of total 25-hydroxyvitamin D, vitamin D-binding protein, and parathyroid hormone as well as bone mineral density (BMD). We genotyped study participants for two common polymorphisms in the vitamin D-binding protein gene (rs7041 and rs4588). We estimated levels of bioavailable 25-hydroxyvitamin D in homozygous participants.
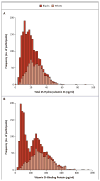
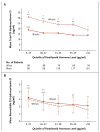
Results: Mean (±SE) levels of both total 25-hydroxyvitamin D and vitamin D-binding protein were lower in blacks than in whites (total 25-hydroxyvitamin D, 15.6±0.2 ng per milliliter vs. 25.8±0.4 ng per milliliter, P<0.001; vitamin D-binding protein, 168±3 μg per milliliter vs. 337±5 μg per milliliter, P<0.001). Genetic polymorphisms independently appeared to explain 79.4% and 9.9% of the variation in levels of vitamin D-binding protein and total 25-hydroxyvitamin D, respectively. BMD was higher in blacks than in whites (1.05±0.01 g per square centimeter vs. 0.94±0.01 g per square centimeter, P<0.001). Levels of parathyroid hormone increased with decreasing levels of total or bioavailable 25-hydroxyvitamin D (P<0.001 for both relationships), yet within each quintile of parathyroid hormone concentration, blacks had significantly lower levels of total 25-hydroxyvitamin D than whites. Among homozygous participants, blacks and whites had similar levels of bioavailable 25-hydroxyvitamin D overall (2.9±0.1 ng per milliliter and 3.1±0.1 ng per milliliter, respectively; P=0.71) and within quintiles of parathyroid hormone concentration.
Conclusions: Community-dwelling black Americans, as compared with whites, had low levels of total 25-hydroxyvitamin D and vitamin D-binding protein, resulting in similar concentrations of estimated bioavailable 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Racial differences in the prevalence of common genetic polymorphisms provide a likely explanation for this observation. (Funded by the National Institute on Aging and others.).
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Berg, Bhan, Karumanchi, and Thadhani report being co-inventors on a patent pending on the use of bioavailable vitamin D for the assessment of vitamin D status. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Comment in
-
Bioavailability of vitamin D and its metabolites in black and white adults.N Engl J Med. 2013 Nov 21;369(21):2047-8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1312291. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 24256384 No abstract available.
-
Assessing vitamin D status: time for a rethink?Clin Chem. 2014 Jun;60(6):809-11. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2013.219386. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Clin Chem. 2014. PMID: 24553058 No abstract available.
-
Vitamin D-binding protein and vitamin D in blacks and whites.N Engl J Med. 2014 Feb 27;370(9):880-1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1315850. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 24571762 No abstract available.
-
Vitamin D-binding protein and vitamin D in blacks and whites.N Engl J Med. 2014 Feb 27;370(9):878. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1315850. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 24571763 No abstract available.
-
Vitamin D-binding protein and vitamin D in blacks and whites.N Engl J Med. 2014 Feb 27;370(9):878-9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1315850. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 24571764 No abstract available.
-
Vitamin D-binding protein and vitamin D in blacks and whites.N Engl J Med. 2014 Feb 27;370(9):879. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1315850. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 24571765 No abstract available.
-
Vitamin D-binding protein and vitamin D in blacks and whites.N Engl J Med. 2014 Feb 27;370(9):879-80. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1315850. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 24571766 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
