Localization and behaviors in null mice suggest that ASIC1 and ASIC2 modulate responses to aversive stimuli
- PMID: 24256442
- PMCID: PMC3998777
- DOI: 10.1111/gbb.12108
Localization and behaviors in null mice suggest that ASIC1 and ASIC2 modulate responses to aversive stimuli
Abstract
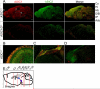
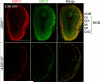
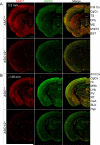
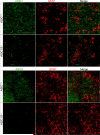
Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) generate H(+) -gated Na(+) currents that contribute to neuronal function and animal behavior. Like ASIC1, ASIC2 subunits are expressed in the brain and multimerize with ASIC1 to influence acid-evoked currents and facilitate ASIC1 localization to dendritic spines. To better understand how ASIC2 contributes to brain function, we localized the protein and tested the behavioral consequences of ASIC2 gene disruption. For comparison, we also localized ASIC1 and studied ASIC1(-/-) mice. ASIC2 was prominently expressed in areas of high synaptic density, and with a few exceptions, ASIC1 and ASIC2 localization exhibited substantial overlap. Loss of ASIC1 or ASIC2 decreased freezing behavior in contextual and auditory cue fear conditioning assays, in response to predator odor and in response to CO2 inhalation. In addition, loss of ASIC1 or ASIC2 increased activity in a forced swim assay. These data suggest that ASIC2, like ASIC1, plays a key role in determining the defensive response to aversive stimuli. They also raise the question of whether gene variations in both ASIC1 and ASIC2 might affect fear and panic in humans.
Keywords: ASIC1; ASIC2; Acid-sensing ion channel; brain; carbon dioxide; fear conditioning; immunocytochemistry.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd and International Behavioural and Neural Genetics Society.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Acid-sensing ion channel 1 is localized in brain regions with high synaptic density and contributes to fear conditioning.J Neurosci. 2003 Jul 2;23(13):5496-502. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-13-05496.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12843249 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of acid-sensing ion channel 2 enhances pulmonary vascular resistance and hypoxic pulmonary hypertension.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019 Aug 1;127(2):393-407. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00894.2018. Epub 2019 Jun 6. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019. PMID: 31169471 Free PMC article.
-
Acid sensing ion channel 2: A new potential player in the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis.Eur J Neurosci. 2019 May;49(10):1233-1243. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14302. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Eur J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30549327 Free PMC article.
-
Acid-Sensing Ion Channels Structural Aspects, Pathophysiological Importance and Experimental Mutational Data Available Across Various Species to Target Human ASIC1.Curr Drug Targets. 2019;20(1):111-121. doi: 10.2174/1389450119666180820103316. Curr Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30124148 Review.
-
Genetic exploration of the role of acid-sensing ion channels.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Jul;94:99-118. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.12.011. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25582292 Review.
Cited by
-
ASIC-dependent LTP at multiple glutamatergic synapses in amygdala network is required for fear memory.Sci Rep. 2015 May 19;5:10143. doi: 10.1038/srep10143. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25988357 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT2A receptor activation is necessary for CO2-induced arousal.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Jul;114(1):233-43. doi: 10.1152/jn.00213.2015. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25925320 Free PMC article.
-
GPR68 Contributes to Persistent Acidosis-Induced Activation of AGC Kinases and Tyrosine Phosphorylation in Organotypic Hippocampal Slices.Front Neurosci. 2021 May 25;15:692217. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.692217. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34113235 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating role of ASIC2 in synaptic and behavioral responses to drugs of abuse.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jan 30;10:1118754. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1118754. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36793786 Free PMC article.
-
Acid-Sensing Ion Channels and Mechanosensation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 1;22(9):4810. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094810. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34062742 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Maren S, Sage JR, Goodrich S, Fanselow MS. Scopolamine and Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats: dose-effect analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21:731–744. - PubMed
-
- Askwith CC, Wemmie JA, Price MP, Rokhlina T, Welsh MJ. Acid-sensing ion channel 2 (ASIC2) modulates ASIC1 H+-activated currents in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:18296–18305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 ES005605/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 5 R01 HL113863-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- 2 UL1 TR000442-06/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HL07121/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS069667/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01MH085724-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000741/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- T32 HL007121/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085724/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

