Insights into the suppressor of T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling-1 (Sts-1)-mediated regulation of TCR signaling through the use of novel substrate-trapping Sts-1 phosphatase variants
- PMID: 24256567
- PMCID: PMC3968691
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.12615
Insights into the suppressor of T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling-1 (Sts-1)-mediated regulation of TCR signaling through the use of novel substrate-trapping Sts-1 phosphatase variants
Abstract
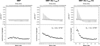
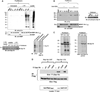
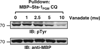
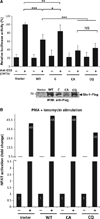
High affinity substrate-trapping protein tyrosine phosphatases have been widely used both to investigate the endogenous targets of many phosphatases and to address questions of substrate specificity. Herein, we extend the concept of a substrate-trapping phosphatase to include an enzyme of the histidine phosphatase superfamily. This is the first description of substrate-trapping technology applied to a member of the histidine phosphatase family. The phosphatase suppressor of T-cell receptor signaling (Sts)-1 has recently been reported to negatively regulate signaling downstream of the T-cell receptor. We generated high-affinity substrate-trapping variants of Sts-1 by mutagenesis of key active site residues within the phosphatase catalytic domain. Mutation of both the nucleophilic His380 and the general acid Glu490 yielded Sts-1 enzymes that were catalytically inactive but showed high affinity for an important tyrosine kinase in T cells that Sts-1 is known to regulate, Zap-70. Sts-1 substrate-trapping mutants isolated tyrosine-phosphorylated Zap-70 from lysates of activated T cells, validating Zap-70 as a possible substrate for Sts-1 and highlighting the efficacy of the mutants as substrate-trapping agents. Inhibition of the Zap-70 interaction by vanadate suggests that the substrate-trapping effect occurred via the Sts-1 phosphatase active site. Finally, overexpression of Sts-1 substrate-trapping mutants in T cells blocked T-cell receptor signaling, confirming the inhibitory effect of Sts-1 on Zap-70.
Keywords: T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling; histidine phosphatase superfamily; suppressor of T-cell receptor signaling (Sts) proteins.
© 2013 FEBS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Samelson LE. Immunoreceptor signaling. In: Cantley L, Hunter T, Sever R, Thorner J, editors. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology: Signal Transduction. Woodbury, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2011.
-
- Deindl S, Kadlecek TA, Brdicka T, Cao X, Weiss A, Kuriyan J. Structural basis for the inhibition of tyrosine kinase activity of Zap-70. Cell. 2007;129:735–746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

