Identification and characterization of functional risk variants for colorectal cancer mapping to chromosome 11q23.1
- PMID: 24256810
- PMCID: PMC3959808
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddt584
Identification and characterization of functional risk variants for colorectal cancer mapping to chromosome 11q23.1
Abstract
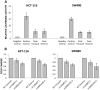
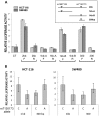
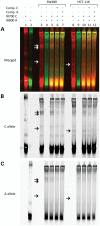
Genome-wide association studies of colorectal cancer (CRC) have identified a number of common variants associated with modest risk, including rs3802842 at chromosome 11q23.1. Several genes map to this region but rs3802842 does not map to any known transcribed or regulatory sequences. We reasoned, therefore, that rs3802842 is not the functional single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), but is in linkage disequilibrium (LD) with a functional SNP(s). We performed ChIP-seq for histone modifications in SW480 and HCT-116 CRC cells, and incorporated ChIP-seq and DNase I hypersensitivity data available through ENCODE within a 137-kb genomic region containing rs3802842 on 11q23.1. We identified SNP rs10891246 in LD with rs3802842 that mapped within a bidirectional promoter region of genes C11orf92 and C11orf93. Following mutagenesis to the risk allele, the promoter demonstrated lower levels of reporter gene expression. A second SNP rs7130173 was identified in LD with rs3802842 that mapped to a candidate enhancer region, which showed strong unidirectional activity in both HCT-116 and SW480 CRC cells. The risk allele of rs7130173 demonstrated reduced enhancer activity compared with the common allele, and reduced nuclear protein binding affinity in electromobility shift assays compared with the common allele suggesting differential transcription factor (TF) binding. SNPs rs10891246 and rs7130173 are on the same haplotype, and expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) analyses of neighboring genes implicate C11orf53, C11orf92 and C11orf93 as candidate target genes. These data imply that rs10891246 and rs7130173 are functional SNPs mapping to 11q23.1 and that C11orf53, C11orf92 and C11orf93 represent novel candidate target genes involved in CRC etiology.
Figures


References
-
- Houlston R.S., Cheadle J., Dobbins S.E., Tenesa A., Jones A.M., Howarth K., Spain S.L., Broderick P., Domingo E., Farrington S., et al. Meta-analysis of three genome-wide association studies identifies susceptibility loci for colorectal cancer at 1q41, 3q26.2, 12q13.13 and 20q13.33. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:973–977. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tomlinson I.P., Webb E., Carvajal-Carmona L., Broderick P., Howarth K., Pittman A.M., Spain S., Lubbe S., Walther A., Sullivan K., et al. A genome-wide association study identifies colorectal cancer susceptibility loci on chromosomes 10p14 and 8q23.3. Nat. Genet. 2008;40:623–630. - PubMed
-
- Tenesa A., Farrington S.M., Prendergast J.G., Porteous M.E., Walker M., Haq N., Barnetson R.A., Theodoratou E., Cetnarskyj R., Cartwright N., et al. Genome-wide association scan identifies a colorectal cancer susceptibility locus on 11q23 and replicates risk loci at 8q24 and 18q21. Nat. Genet. 2008;40:631–637. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tomlinson I., Webb E., Carvajal-Carmona L., Broderick P., Kemp Z., Spain S., Penegar S., Chandler I., Gorman M., Wood W., et al. A genome-wide association scan of tag SNPs identifies a susceptibility variant for colorectal cancer at 8q24.21. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:984–988. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

