Two surfaces of cytochrome b5 with major and minor contributions to CYP3A4-catalyzed steroid and nifedipine oxygenation chemistries
- PMID: 24256945
- PMCID: PMC3933929
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2013.11.001
Two surfaces of cytochrome b5 with major and minor contributions to CYP3A4-catalyzed steroid and nifedipine oxygenation chemistries
Abstract
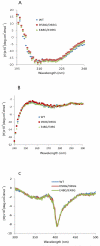
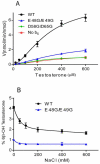
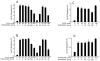
Conserved human cytochrome b5 (b5) residues D58 and D65 are critical for interactions with CYP2E1 and CYP2C19, whereas E48 and E49 are essential for stimulating the 17,20-lyase activity of CYP17A1. Here, we show that b5 mutations E48G, E49G, D58G, and D65G have reduced capacity to stimulate CYP3A4-catalyzed progesterone and testosterone 6β-hydroxylation or nifedipine oxidation. The b5 double mutation D58G/D65G fails to stimulate these reactions, similar to CYP2E1 and CYP2C19, whereas mutation E48G/E49G retains 23-42% of wild-type stimulation. Neither mutation impairs the activity stimulation of wild-type b5, nor does mutation D58G/D65G impair the partial stimulation of mutations E48G or E48G/E49G. For assays reconstituted with a single phospholipid, phosphatidyl serine afforded the highest testosterone 6β-hydroxylase activity with wild-type b5 but the poorest activity with b5 mutation E48G/E49G, and the activity stimulation of mutation E48G/E49G was lost at [NaCl]>50mM. Cross-linking of CYP3A4 and b5 decreased in the order wild-type>E48G/E49G>D58G/D65G and varied with phospholipid. We conclude that two b5 acidic surfaces, primarily the domain including residues D58-D65, participate in the stimulation of CYP3A4 activities. Our data suggest that a minor population of CYP3A4 molecules remains sensitive to b5 mutation E48G/E49G, consistent with phospholipid-dependent conformational heterogeneity of CYP3A4.
Keywords: Allostery; CYP3A4; Cytochrome P450; Cytochrome b(5); Drug oxidation; Testosterone.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


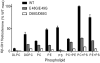
Similar articles
-
The action of cytochrome b(5) on CYP2E1 and CYP2C19 activities requires anionic residues D58 and D65.Biochemistry. 2013 Jan 8;52(1):210-20. doi: 10.1021/bi301384n. Epub 2012 Dec 17. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23193974 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytochrome b5 requires residues E48 and E49 to stimulate the 17,20-lyase activity of cytochrome P450c17.Biochemistry. 2006 Jan 24;45(3):755-62. doi: 10.1021/bi051623y. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16411751
-
Reconstitution of recombinant cytochrome P450 2C10(2C9) and comparison with cytochrome P450 3A4 and other forms: effects of cytochrome P450-P450 and cytochrome P450-b5 interactions.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1997 Jun 15;342(2):329-37. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1997.0125. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1997. PMID: 9186495
-
A Homodimer Model Can Resolve the Conundrum as to How Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase and Cytochrome b5 Compete for the Same Binding Site on Cytochrome P450c17.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017;18(5):515-521. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666161220142957. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017. PMID: 28000554 Review.
-
Role of cytochrome b5 in the modulation of the enzymatic activities of cytochrome P450 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase (P450 17A1).J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Jun;170:2-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.02.033. Epub 2016 Mar 11. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 26976652 Review.
Cited by
-
Catalytic modulation of human cytochromes P450 17A1 and P450 11B2 by phospholipid.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Jul;181:63-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Mar 13. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29548669 Free PMC article.
-
Catalytically relevant electrostatic interactions of cytochrome P450c17 (CYP17A1) and cytochrome b5.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 5;289(49):33838-49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.608919. Epub 2014 Oct 14. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25315771 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional effects of cytochrome b5 interactions with human cytochrome P450 enzymes.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 22;292(51):20818-20833. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000220. Epub 2017 Oct 27. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29079577 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand accessibility to heme cytochrome b5 coordinating sphere and enzymatic activity enhancement upon tyrosine ionization.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2019 May;24(3):317-330. doi: 10.1007/s00775-019-01649-2. Epub 2019 Mar 5. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 30838452
-
Pi-pi Stacking Mediated Cooperative Mechanism for Human Cytochrome P450 3A4.Molecules. 2015 Apr 24;20(5):7558-73. doi: 10.3390/molecules20057558. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25919277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shimada T, Yamazaki H, Mimura M, Inui Y, Guengerich FP. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;270:414–423. - PubMed
-
- Abel SM, Back DJ. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1993;46:827–832. - PubMed
-
- Waxman DJ, Attisano C, Guengerich FP, Lapenson DP. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988;263:424–436. - PubMed
-
- Kerlan V, Dreano Y, Bercovici JP, Beaune PH, Floch HH, Berthou F. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992;44:1745–1756. - PubMed
-
- Yamazaki H, Gillam EM, Dong MS, Johnson WW, Guengerich FP, Shimada T. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1997;342:329–337. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

