Antibody VH and VL recombination using phage and ribosome display technologies reveals distinct structural routes to affinity improvements with VH-VL interface residues providing important structural diversity
- PMID: 24256948
- PMCID: PMC3929446
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.27261
Antibody VH and VL recombination using phage and ribosome display technologies reveals distinct structural routes to affinity improvements with VH-VL interface residues providing important structural diversity
Abstract
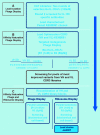
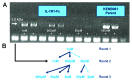
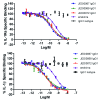
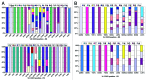
In vitro selection technologies are an important means of affinity maturing antibodies to generate the optimal therapeutic profile for a particular disease target. Here, we describe the isolation of a parent antibody, KENB061 using phage display and solution phase selections with soluble biotinylated human IL-1R1. KENB061 was affinity matured using phage display and targeted mutagenesis of VH and VL CDR3 using NNS randomization. Affinity matured VHCDR3 and VLCDR3 library blocks were recombined and selected using phage and ribosome display protocol. A direct comparison of the phage and ribosome display antibodies generated was made to determine their functional characteristics.In our analyses, we observed distinct differences in the pattern of beneficial mutations in antibodies derived from phage and ribosome display selections, and discovered the lead antibody Jedi067 had a ~3700-fold improvement in KD over the parent KENB061. We constructed a homology model of the Fv region of Jedi067 to map the specific positions where mutations occurred in the CDR3 loops. For VL CDR3, positions 94 to 97 carry greater diversity in the ribosome display variants compared with the phage display. The positions 95a, 95b and 96 of VLCDR3 form part of the interface with VH in this model. The model shows that positions 96, 98, 100e, 100f, 100 g, 100h, 100i and 101 of the VHCDR3 include residues at the VH and VL interface. Importantly, Leu96 and Tyr98 are conserved at the interface positions in both phage and ribosome display indicating their importance in maintaining the VH-VL interface. For antibodies derived from ribosome display, there is significant diversity at residues 100a to 100f of the VH CDR3 compared with phage display. A unique deletion of isoleucine at position 102 of the lead candidate, Jedi067, also occurs in the VHCDR3.As anticipated, recombining the mutations via ribosome display led to a greater structural diversity, particularly in the heavy chain CDR3, which in turn led to antibodies with improved potencies. For this particular analysis, we also found that VH-VL interface positions provided a source of structural diversity for those derived from the ribosome display selections. This greater diversity is a likely consequence of the presence of a larger pool of recombinants in the ribosome display system, or the evolutionary capacity of ribosome display, but may also reflect differential selection of antibodies in the two systems.
Figures

References
-
- Wilkinson T, Lowe D, Vaughan TJ. Affinity maturation approaches for antibody lead optimization. In Antibody drug discovery 2013; (Wood, C. R., ed.): pp. 85, IMPERIAL COLLEGE PRESS.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
