Age dependency of vasopressin pulmonary vasodilatory effect in rats
- PMID: 24257319
- PMCID: PMC3986081
- DOI: 10.1038/pr.2013.221
Age dependency of vasopressin pulmonary vasodilatory effect in rats
Abstract
Background: Vasopressin is a systemic vasoconstrictor. Its pulmonary vasodilatory effect is controversial, and limited data are available on its use in neonates with pulmonary hypertension. Hypothesizing that the vasopressin-induced pulmonary vasodilation is developmentally regulated, we evaluated its pulmonary and systemic arterial response in newborn and adult rats.
Methods: Vessels were mounted on a wire myograph, and the vasopressin-induced changes in vasomotor tone measured. The vessel- and age-dependent differences in vasopressin V1a and V2 receptors' expression were evaluated by western blotting.
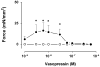
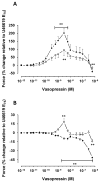
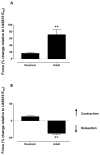
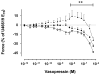
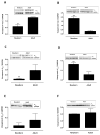
Results: Vasopressin induced a dose-dependent increase in mesenteric arterial tone at both ages, but of greater magnitude in adult vessels (P < 0.01). At lower concentrations, vasopressin induced pulmonary vasodilation in adult vessels and vasoconstriction in newborn arteries. The adult vasopressin-induced pulmonary vasodilation was inhibited by ibuprofen, suggesting that the response is prostaglandin mediated. Pulmonary tissue V1a receptor protein expression was higher in adult, when compared with newborn arteries (P < 0.01). The adult vessels V1a expression predominated in the pulmonary arteries, and V2 was only detected in mesenteric arteries.
Conclusion: The vasopressin-induced pulmonary vasodilation is absent in newborn rats likely due to the lower tissue V1a expression early in life. These animal data challenge the therapeutic use of vasopressin in neonatal pulmonary hypertension.
Figures
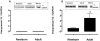
Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide, but not vasopressin V2 receptor-mediated vasodilation, modulates vasopressin-induced renal vasoconstriction in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000 Mar;361(3):319-26. doi: 10.1007/s002109900187. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10731046
-
Lack of effect of a selective vasopressin V1A receptor antagonist SR 49,059, on potentiation by vasopressin of adrenoceptor-mediated pressor responses in the rat mesenteric arterial bed.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Nov;125(6):1120-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702167. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9863637 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired vasoconstriction and nitric oxide-mediated relaxation in pulmonary arteries of hypoxia- and monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertensive rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Feb;332(2):455-62. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.160119. Epub 2009 Nov 13. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 19915069 Free PMC article.
-
Control of the renal medullary circulation by vasopressin V1 and V2 receptors in the rat.Exp Physiol. 2000 Mar;85 Spec No:223S-231S. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-445x.2000.tb00027.x. Exp Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10795926 Review.
-
Discovery and design of novel and selective vasopressin and oxytocin agonists and antagonists: the role of bioassays.Exp Physiol. 2000 Mar;85 Spec No:7S-18S. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-445x.2000.tb00003.x. Exp Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10795902 Review.
Cited by
-
Pulmonary Hypertension in Intensive Care Units: An Updated Review.Tanaffos. 2019 Mar;18(3):180-207. Tanaffos. 2019. PMID: 32411259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Masked Randomized Trial of Epinephrine versus Vasopressin in an Ovine Model of Perinatal Cardiac Arrest.Children (Basel). 2023 Feb 10;10(2):349. doi: 10.3390/children10020349. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36832479 Free PMC article.
-
Vasopressin and Breathing: Review of Evidence for Respiratory Effects of the Antidiuretic Hormone.Front Physiol. 2021 Oct 26;12:744177. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.744177. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34867449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iatrogenic bleeding during flexible bronchoscopy: risk factors, prophylactic measures and management.ERJ Open Res. 2017 Jun 21;3(2):00084-2016. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00084-2016. eCollection 2017 Apr. ERJ Open Res. 2017. PMID: 28656131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of vasopressin during a pulmonary hypertensive crisis induced by acute hypoxia in a rat model of pulmonary hypertension.Br J Anaesth. 2019 Apr;122(4):437-447. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2019.01.014. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Br J Anaesth. 2019. PMID: 30857600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharman A, Low J. Vasopressin and its role in critical care. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia, Critical Care & Pain. 2008;8:134–137.
-
- Tayama E, Ueda T, Shojima T, Akasu K, Oda T, Fukunaga S, Akashi H, Aoyagi S. Arginine vasopressin is an ideal drug after cardiac surgery for the management of low systemic vascular resistant hypotension concomitant with pulmonary hypertension. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2007;6:715–719. - PubMed
-
- Smith AM, Elliot CM, Kiely DG, Channer KS. The role of vasopressin in cardiorespiratory arrest and pulmonary hypertension. QJM. 2006;99:127–133. - PubMed
-
- Scheurer MA, Bradley SM, Atz AM. Vasopressin to attenuate pulmonary hypertension and improve systemic blood pressure after correction of obstructed total anomalous pulmonary venous return. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129:464–466. - PubMed
-
- Sai Y, Okamura T, Amakata Y, Toda N. Comparison of responses of canine pulmonary artery and vein to angiotensin II, bradykinin and vasopressin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;282:235–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

