Evolutionary conservation of primate lymphocryptovirus microRNA targets
- PMID: 24257599
- PMCID: PMC3911612
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02071-13
Evolutionary conservation of primate lymphocryptovirus microRNA targets
Abstract
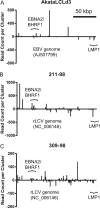
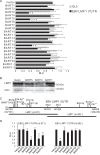
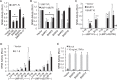
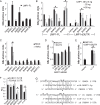
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and rhesus lymphocryptovirus (rLCV) are closely related gammaherpesviruses in the lymphocryptovirus subgroup that express viral microRNAs (miRNAs) during latent infection. In addition to many host mRNAs, EBV miRNAs are known to target latent viral transcripts, specifically those encoding LMP1, BHRF1, and EBNA2. The mRNA targets of rLCV miRNAs have not been investigated. Using luciferase reporter assays, photoactivatable cross-linking and immunoprecipitation (PAR-CLIP), and deep sequencing, we demonstrate that posttranscriptional regulation of LMP1 expression is a conserved function of lymphocryptovirus miRNAs. Furthermore, the mRNAs encoding the rLCV EBNA2 and BHRF1 homologs are regulated by miRNAs in rLCV-infected B cells. Homologous to sites in the EBV LMP1 and BHRF1 3'-untranslated regions (UTRs), we also identified evolutionarily conserved binding sites for the cellular miR-17/20/106 family in the LMP1 and BHRF1 3'UTRs of several primate LCVs. Finally, we investigated the functional consequences of LMP1 targeting by individual EBV BART miRNAs and show that select viral miRNAs play a role in the previously observed modulation of NF-κB activation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr Virus miR-BHRF1-3 Targets the BZLF1 3'UTR and Regulates the Lytic Cycle.J Virol. 2022 Feb 23;96(4):e0149521. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01495-21. Epub 2021 Dec 8. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34878852 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB Signaling Regulates Expression of Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.J Virol. 2016 Jun 24;90(14):6475-88. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00613-16. Print 2016 Jul 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27147748 Free PMC article.
-
A global analysis of evolutionary conservation among known and predicted gammaherpesvirus microRNAs.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(2):716-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01302-09. Epub 2009 Nov 4. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19889779 Free PMC article.
-
Non-human Primate Lymphocryptoviruses: Past, Present, and Future.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:385-405. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_13. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428382 Review.
-
Genetics of Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs.Semin Cancer Biol. 2014 Jun;26:52-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.02.002. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014. PMID: 24602823 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive profiling of functional Epstein-Barr virus miRNA expression in human cell lines.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 17;17:644. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2978-6. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27531524 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the NFκb Signalling Pathway by Human Cytomegalovirus.Virology (Hyderabad). 2017 Aug;1(1):104. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Virology (Hyderabad). 2017. PMID: 29082387 Free PMC article.
-
EBV BART MicroRNAs Target Multiple Pro-apoptotic Cellular Genes to Promote Epithelial Cell Survival.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Jun 12;11(6):e1004979. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004979. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26070070 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs regulate B cell receptor signal transduction and lytic reactivation.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jan 7;15(1):e1007535. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007535. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30615681 Free PMC article.
-
Viral MicroRNAs: Interfering the Interferon Signaling.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(4):446-454. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200109181238. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 31924149 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

