Efficacy and safety of vortioxetine (Lu AA21004), 15 and 20 mg/day: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, duloxetine-referenced study in the acute treatment of adult patients with major depressive disorder
- PMID: 24257717
- PMCID: PMC3979887
- DOI: 10.1097/YIC.0000000000000018
Efficacy and safety of vortioxetine (Lu AA21004), 15 and 20 mg/day: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, duloxetine-referenced study in the acute treatment of adult patients with major depressive disorder
Abstract
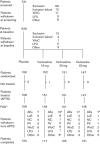
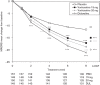
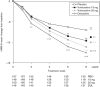
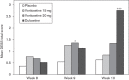
This study assessed the efficacy, tolerability and safety of vortioxetine versus placebo in adults with recurrent major depressive disorder. This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study included 608 patients [Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) total score ≥ 26 and Clinical Global Impression - Severity score ≥ 4]. Patients were randomly assigned (1 : 1 : 1 : 1) to vortioxetine 15 mg/day, vortioxetine 20 mg/day, duloxetine 60 mg/day or placebo. The primary efficacy endpoint was change from baseline in MADRS total score at week 8 (mixed model for repeated measurements). Key secondary endpoints were: MADRS responders; Clinical Global Impression - Improvement scale score; MADRS total score in patients with baseline Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale ≥ 20; remission (MADRS ≤ 10); and Sheehan Disability Scale total score at week 8. On the primary efficacy endpoint, both vortioxetine doses were statistically significantly superior to placebo, with a mean difference to placebo (n = 158) of -5.5 (vortioxetine 15 mg, P < 0.0001, n = 149) and -7.1 MADRS points (vortioxetine 20 mg, P < 0.0001, n = 151). Duloxetine (n = 146) separated from placebo, thus validating the study. In all key secondary analyses, both vortioxetine doses were statistically significantly superior to placebo. Vortioxetine treatment was well tolerated; common adverse events (incidence ≥ 5%) were nausea, headache, diarrhea, dry mouth and dizziness. No clinically relevant changes were seen in clinical safety laboratory values, weight, ECG or vital signs parameters. Vortioxetine was efficacious and well tolerated in the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01140906.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, text revision (DSM-IV-TR) 2000:4th ed.Washington DC:American Psychiatric Association
-
- Areberg J, Chen G, Naik H, Pedersen KB, Vakilynejad M.A population pharmacokinetic meta-analysis of vortioxetine (Lu AA21004) in healthy subjects.Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract 2012a;16Suppl 115
-
- Areberg J, Luntang-Jensen M, Søgaard B, Nilausen DO.Occupancy of the serotonin transporter after administration of Lu AA21004 and its relation to plasma concentration in healthy subjects.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2012b;110:401–404 - PubMed
-
- Baldwin DS.Sexual dysfunction associated with antidepressant drugs.Expert Opin Drug Saf 2004;3:457–470 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

