CD4 and BST-2/tetherin proteins retro-translocate from endoplasmic reticulum to cytosol as partially folded and multimeric molecules
- PMID: 24257748
- PMCID: PMC3879533
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.512368
CD4 and BST-2/tetherin proteins retro-translocate from endoplasmic reticulum to cytosol as partially folded and multimeric molecules
Abstract
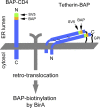
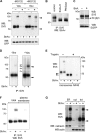
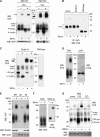
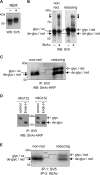
CD4 and BST-2/Tetherin are cellular membrane proteins targeted to degradation by the HIV-1 protein Vpu. In both cases proteasomal degradation following recruitment into the ERAD pathway has been described. CD4 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein, with four extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains containing three intrachain disulfide bridges. BST-2/Tetherin is an atypical type II transmembrane glycoprotein with an N-terminal transmembrane domain and a C-terminal glycophosphatidylinositol anchor, which dimerizes through three interchain bridges. We investigated spontaneous and Vpu-induced retro-translocation of CD4 and BST-2/Tetherin using our novel biotinylation technique in living cells to determine ER-to-cytosol retro-translocation of proteins. We found that CD4 retro-translocates with oxidized intrachain disulfide bridges, and only upon proteasomal inhibition does it accumulate in the cytosol as already reduced and deglycosylated molecules. Similarly, BST-2/Tetherin is first exposed to the cytosol as a dimeric oxidized complex and then becomes deglycosylated and reduced to monomers. These results raise questions on the required features of the putative retro-translocon, suggesting alternative retro-translocation mechanisms for membrane proteins in which complete cysteine reduction and unfolding are not always strictly required before ER to cytosol dislocation.
Keywords: BST-2; Biotin; Biotinylation; CD4; Disulfide; ER-associated Degradation; ERAD; Oxidation-Reduction; Retro-translocation; Tetherin.
Figures


References
-
- Ghaemmaghami S., Huh W. K., Bower K., Howson R. W., Belle A., Dephoure N., O'Shea E. K., Weissman J. S. (2003) Global analysis of protein expression in yeast. Nature 425, 737–741 - PubMed
-
- Rapoport T. A. (2007) Protein translocation across the eukaryotic endoplasmic reticulum and bacterial plasma membranes. Nature 450, 663–669 - PubMed
-
- Geiger R., Andritschke D., Friebe S., Herzog F., Luisoni S., Heger T., Helenius A. (2011) BAP31 and BiP are essential for dislocation of SV40 from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol. Nat. Cell Biol. 13, 1305–1314 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

