Arrestin-3 binds c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) and JNK2 and facilitates the activation of these ubiquitous JNK isoforms in cells via scaffolding
- PMID: 24257757
- PMCID: PMC3873585
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.510412
Arrestin-3 binds c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) and JNK2 and facilitates the activation of these ubiquitous JNK isoforms in cells via scaffolding
Abstract
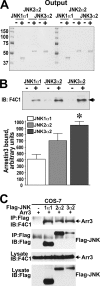
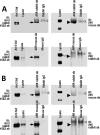
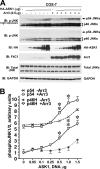
Non-visual arrestins scaffold mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades. The c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) are members of MAPK family. Arrestin-3 has been shown to enhance the activation of JNK3, which is expressed mainly in neurons, heart, and testes, in contrast to ubiquitous JNK1 and JNK2. Although all JNKs are activated by MKK4 and MKK7, both of which bind arrestin-3, the ability of arrestin-3 to facilitate the activation of JNK1 and JNK2 has never been reported. Using purified proteins we found that arrestin-3 directly binds JNK1α1 and JNK2α2, interacting with the latter comparably to JNK3α2. Phosphorylation of purified JNK1α1 and JNK2α2 by MKK4 or MKK7 is increased by arrestin-3. Endogenous arrestin-3 interacted with endogenous JNK1/2 in different cell types. Arrestin-3 also enhanced phosphorylation of endogenous JNK1/2 in intact cells upon expression of upstream kinases ASK1, MKK4, or MKK7. We observed a biphasic effect of arrestin-3 concentrations on phosphorylation of JNK1α1 and JNK2α2 both in vitro and in vivo. Thus, arrestin-3 acts as a scaffold, facilitating JNK1α1 and JNK2α2 phosphorylation by MKK4 and MKK7 via bringing JNKs and their activators together. The data suggest that arrestin-3 modulates the activity of ubiquitous JNK1 and JNK2 in non-neuronal cells, impacting the signaling pathway that regulates their proliferation and survival.
Keywords: Arrestin; Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK); MAP Kinases (MAPKs); Protein Phosphorylation; Scaffold Proteins; Signal Transduction.
Figures




Similar articles
-
JNK3 enzyme binding to arrestin-3 differentially affects the recruitment of upstream mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinases.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 4;288(40):28535-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.508085. Epub 2013 Aug 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23960075 Free PMC article.
-
Arrestin-3-Dependent Activation of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinases (JNKs).Curr Protoc. 2023 Sep;3(9):e839. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.839. Curr Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37668419 Free PMC article.
-
The beta-arrestin-2 scaffold protein promotes c-Jun N-terminal kinase-3 activation by binding to its nonconserved N terminus.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 6;283(23):15903-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710006200. Epub 2008 Apr 11. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18408005 Free PMC article.
-
Brain JNK and metabolic disease.Diabetologia. 2021 Feb;64(2):265-274. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05327-w. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Diabetologia. 2021. PMID: 33200240 Review.
-
Physiological roles of MKK4 and MKK7: insights from animal models.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Aug;1773(8):1349-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.10.016. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17157936 Review.
Cited by
-
β-Arrestin Based Receptor Signaling Paradigms: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Complex Age-Related Disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 28;9:1369. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01369. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30546309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arrestin-dependent activation of JNK family kinases.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;219:259-80. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41199-1_13. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24292834 Free PMC article.
-
Arrestin-3 interaction with maternal embryonic leucine-zipper kinase.Cell Signal. 2019 Nov;63:109366. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109366. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Cell Signal. 2019. PMID: 31352007 Free PMC article.
-
Arrestin-3 scaffolding of the JNK3 cascade suggests a mechanism for signal amplification.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jan 15;116(3):810-815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1819230116. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30591558 Free PMC article.
-
Arrestin-3 binds the MAP kinase JNK3α2 via multiple sites on both domains.Cell Signal. 2014 Apr;26(4):766-76. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.001. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24412749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gurevich V. V., Gurevich E. V. (2004) The molecular acrobatics of arrestin activation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 25, 105–111 - PubMed
-
- Carman C. V., Benovic J. L. (1998) G-protein-coupled receptors. Turn-ons and turn-offs. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 8, 335–344 - PubMed
-
- DeWire S. M., Ahn S., Lefkowitz R. J., Shenoy S. K. (2007) β-Arrestins and cell signaling. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 69, 483–510 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

