Smc5/6-mediated regulation of replication progression contributes to chromosome assembly during mitosis in human cells
- PMID: 24258023
- PMCID: PMC3890350
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E13-01-0020
Smc5/6-mediated regulation of replication progression contributes to chromosome assembly during mitosis in human cells
Abstract
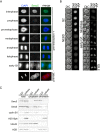
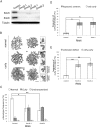
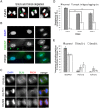
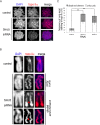
The structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) proteins constitute the core of critical complexes involved in structural organization of chromosomes. In yeast, the Smc5/6 complex is known to mediate repair of DNA breaks and replication of repetitive genomic regions, including ribosomal DNA loci and telomeres. In mammalian cells, which have diverse genome structure and scale from yeast, the Smc5/6 complex has also been implicated in DNA damage response, but its further function in unchallenged conditions remains elusive. In this study, we addressed the behavior and function of Smc5/6 during the cell cycle. Chromatin fractionation, immunofluorescence, and live-cell imaging analyses indicated that Smc5/6 associates with chromatin during interphase but largely dissociates from chromosomes when they condense in mitosis. Depletion of Smc5 and Smc6 resulted in aberrant mitotic chromosome phenotypes that were accompanied by the abnormal distribution of topoisomerase IIα (topo IIα) and condensins and by chromosome segregation errors. Importantly, interphase chromatin structure indicated by the premature chromosome condensation assay suggested that Smc5/6 is required for the on-time progression of DNA replication and subsequent binding of topo IIα on replicated chromatids. These results indicate an essential role of the Smc5/6 complex in processing DNA replication, which becomes indispensable for proper sister chromatid assembly in mitosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic localization of SMC5/6 complex proteins during mammalian meiosis and mitosis suggests functions in distinct chromosome processes.J Cell Sci. 2013 Sep 15;126(Pt 18):4239-52. doi: 10.1242/jcs.130195. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23843628 Free PMC article.
-
SMC5 and SMC6 genes are required for the segregation of repetitive chromosome regions.Nat Cell Biol. 2005 Apr;7(4):412-9. doi: 10.1038/ncb1239. Epub 2005 Mar 27. Nat Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15793567
-
H2A.Z-dependent regulation of cohesin dynamics on chromosome arms.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jun;34(11):2092-104. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00193-14. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24687850 Free PMC article.
-
Genome control by SMC complexes.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Sep;24(9):633-650. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00609-8. Epub 2023 May 25. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37231112 Review.
-
The unnamed complex: what do we know about Smc5-Smc6?Chromosome Res. 2009;17(2):251-63. doi: 10.1007/s10577-008-9016-8. Chromosome Res. 2009. PMID: 19308705 Review.
Cited by
-
SMC5/6: Multifunctional Player in Replication.Genes (Basel). 2018 Dec 22;10(1):7. doi: 10.3390/genes10010007. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30583551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction between NSMCE4A and GPS1 links the SMC5/6 complex to the COP9 signalosome.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2020 May 8;21(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12860-020-00278-x. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32384871 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis NSE4 Proteins Act in Somatic Nuclei and Meiosis to Ensure Plant Viability and Fertility.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Jun 20;10:774. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00774. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31281325 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional mutation of Smc5 in mouse embryonic stem cells perturbs condensin localization and mitotic progression.J Cell Sci. 2016 Apr 15;129(8):1619-34. doi: 10.1242/jcs.179036. Epub 2016 Feb 26. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 26919979 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin association of the SMC5/6 complex is dependent on binding of its NSE3 subunit to DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Feb 18;44(3):1064-79. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1021. Epub 2015 Oct 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26446992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumann C, Korner R, Hofmann K, Nigg EA. PICH, a centromere-associated SNF2 family ATPase, is regulated by Plk1 and required for the spindle checkpoint. Cell. 2007;128:101–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

