Retrospective study of prenatal diagnosed pulmonary sequestration
- PMID: 24258515
- PMCID: PMC5814128
- DOI: 10.1007/s00383-013-3434-1
Retrospective study of prenatal diagnosed pulmonary sequestration
Abstract
Purpose: To describe the prenatal findings, treatments and outcomes of fetuses with pulmonary sequestrations (PS), which were retrospectively studied.
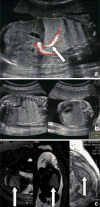
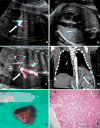
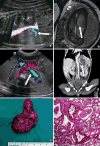
Methods: From May 2010 to January 2013, 292 women were referred to the Guangdong Women and Children Hospital, Guangzhou because obstetric ultrasound had demonstrated fetal lung lesions. In 68 fetuses, the echogenic lung masses were pulmonary sequestrations deriving arterial blood supply from clearly identifiable systemic arteries rather than the pulmonary artery. We examined records of the 68 fetuses and measured the lesions and congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation volume ratio (CVR), provided prenatal counseling and treatment, documented the CVR, location of lesion, gestational age at diagnosis, need for fetal intervention, perinatal clinical course (including the development of hydrops, effusions, and neonatal respiratory distress), gestational age at delivery, postnatal ultrasound and CT, operation treatment, survival and pathology.
Results: There were 68 PS in our study. All of 56 cases with CVR ≤ 1.6, survived without prenatal hydrops or postnatal respiratory symptoms. In 12 cases with CVR >1.6, 7 cases (58.3 %, 7/12) had hydrops, 10 cases (83.3 %, 10/12) survived, 2 cases (16.7 %, 2/12) of induced abortion, 8 cases (66 %, 8/12) were postnatal symptomatic. There was statistical significant difference in the incidence rate of hydrops and postnatal respiratory symptoms between the PS with CVR ≤ 1.6 and that with CVR >1.6. 66 cases postnatal survived, two cases of induced abortion. 64 cases had no prenatal treatment, two cases underwent thoracoamniotic shunt. The mean gestational age at birth was 38 weeks (range 34-40 weeks). 21 asymptomatic cases had no surgery. 45 cases (8 symptomatic and 37 asymptomatic) underwent surgical resections, 43 cases without postoperative complications, two cases of postoperative pneumothorax, no wound infection. Postoperative follow-up showed good growth in all surgery cases.
Conclusion: PS specific absence of hydrop was a congenital disorder with an excellent prognosis. CVR >1.6 was associated with fetal hydrops and postnatal symptoms. However, absolute CVR value cannot be used to select fetuses for fetal treatment before the development of hydrops. Surgery of PS in neonates or infants presented a good outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Harriet JC, Gillian MH. Pulmonary sequestration. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2004;5:59–68. - PubMed
-
- Pryce DM. Lower accessory pulmonary artery with intralobar sequestration of the lung: report of cases. J Pathol. 1946;58:457–467. - PubMed
-
- Gezer S, Tastepe I, Sirmali M, et al. Pulmonary sequestration: a single-institutional series composed of 27 cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;133:955–959. - PubMed
-
- Cooke CR. Bronchopulmonary sequestration. Respir Care. 2006;51:661–664. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

