Metformin is associated with survival benefit in cancer patients with concurrent type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24258613
- PMCID: PMC3868417
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0111
Metformin is associated with survival benefit in cancer patients with concurrent type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Patients with type 2 diabetes have increased cancer risk and cancer-related mortality, which can be reduced by metformin treatment. However, it is unclear whether metformin can also modulate clinical outcomes in patients with cancer and concurrent type 2 diabetes.
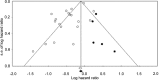
Patients and methods: A meta-analysis of 20 publications that included 13,008 subjects was performed to investigate the association between metformin and overall survival (OS) as well as cancer-specific survival (CSS) in patients with cancer and concurrent type 2 diabetes.
Results: We found that there was a relative survival benefit associated with metformin treatment compared with treatment with other glucose-lowering medications in both OS and CSS (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.66; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.55-0.79 and HR = 0.62; 95% CI: 0.46-0.84, respectively). These associations were also observed in subgroups by cancer type and country.
Conclusion: These results suggest that metformin is the drug of choice in the treatment of patients with cancer and concurrent type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Cancer; Diabetes; Meta-Analysis; Metformin; Survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of potential conflicts of interest may be found at the end of this article.
Figures

Comment in
-
Metformin: are potential benefits on cancer risk extended to cancer survival?Oncologist. 2013;18(12):1245-7. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0381. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Oncologist. 2013. PMID: 24258614 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Richardson LC, Pollack LA. Therapy insight: Influence of type 2 diabetes on the development, treatment and outcomes of cancer. Nat Clin Prac. 2005;2:48–53. - PubMed
-
- Kim YD, Park KG, Lee YS, et al. Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis through amp-activated protein kinase-dependent regulation of the orphan nuclear receptor shp. Diabetes. 2008;57:306–314. - PubMed
-
- Staels B. Metformin and pioglitazone: Effectively treating insulin resistance. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006;22(Suppl 2):27–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

