A novel germline PIGA mutation in Ferro-Cerebro-Cutaneous syndrome: a neurodegenerative X-linked epileptic encephalopathy with systemic iron-overload
- PMID: 24259288
- PMCID: PMC4349522
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36189
A novel germline PIGA mutation in Ferro-Cerebro-Cutaneous syndrome: a neurodegenerative X-linked epileptic encephalopathy with systemic iron-overload
Abstract
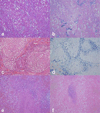
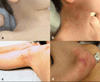
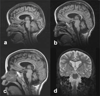
Three related males presented with a newly recognized x-linked syndrome associated with neurodegeneration, cutaneous abnormalities, and systemic iron overload. Linkage studies demonstrated that they shared a haplotype on Xp21.3-Xp22.2 and exome sequencing was used to identify candidate variants. Of the segregating variants, only a PIGA mutation segregated with disease in the family. The c.328_330delCCT PIGA variant predicts, p.Leu110del (or c.1030_1032delCTT, p.Leu344del depending on the reference sequence). The unaffected great-grandfather shared his X allele with the proband but he did not have the PIGA mutation, indicating that the mutation arose de novo in his daughter. A single family with a germline PIGA mutation has been reported; affected males had a phenotype characterized by multiple congenital anomalies and severe neurologic impairment resulting in infantile lethality. In contrast, affected boys in the family described here were born without anomalies and were neurologically normal prior to onset of seizures after 6 months of age, with two surviving to the second decade. PIGA encodes an enzyme in the GPI anchor biosynthesis pathway. An affected individual in the family studied here was deficient in GPI anchor proteins on granulocytes but not erythrocytes. In conclusion, the PIGA mutation in this family likely causes a reduction in GPI anchor protein cell surface expression in various cell types, resulting in the observed pleiotropic phenotype involving central nervous system, skin, and iron metabolism.
Keywords: Ferro-Cerebro-Cutaneous syndrome; PIG-A protein; PIGA; X-linked; cerebellar atrophy; encephalopathy; epilepsy; exome; hemochromatosis; iron; microcephaly; neurodegeneration; recessive; seizures; sequencing.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: KJS has received grant funding from the National Institutes of Child Health and Disease, the National Institutes of Neurologic Disease and Stroke, the Muscular Dystrophy Association and the Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood Foundation. She has clinical trial contracts with ISIS Pharmaceuticals and Biomarin. She has served as a paid consultant to Novartis and BioLife Stem Cell. The other authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures








Comment in
-
Invited editorial comment--The human phenotype of germline PIGA mutations.Am J Med Genet A. 2014 Jan;164A(1):15-6. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36213. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Am J Med Genet A. 2014. PMID: 24273085
References
-
- Almeida AM, Murakami Y, Layton DM, Hillmen P, Sellick GS, Maeda Y, Richards S, Patterson S, Kotsianidis I, Mollica L, Crawford DH, Baker A, Ferguson M, Roberts I, Houlston R, Kinoshita T, Karadimitris A. Hypomorphic promoter mutation in PIGM causes inherited glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol deficiency. Nat Med. 2006;12:846–851. - PubMed
-
- Almeida AM, Murakami Y, Baker A, Maeda Y, Roberts IA, Kinoshita T, Layton DM, Karadimitris A. Targeted therapy for inherited GPI deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1641–1647. - PubMed
-
- Collardeau-Frachon S, Heissat S, Bouvier R, Fabre M, Baruteau J, Broue P, Cordier MP, Debray D, Debiec H, Ronco P, Guigonis V. A French retrospective multicentric study of neonatal hemochromatosis: Importance of autopsy and of auto-immune maternal manifestations. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2012;15:450–470. - PubMed
-
- DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C, Philippakis AA, del Angel G, Rivas MA, Hanna M, McKenna A, Fennell TJ, Kernytsky AM, Sivachenko AY, Cibulskis K, Gabriel SB, Altshuler D, Daly MJ. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet. 2011;43:491–498. - PMC - PubMed
-
- González-Vioque E, Blázquez A, Fernández-Moreira D, Bornstein B, Bautista J, Arpa J, Navarro C, Campos Y, Fernández-Moreno MA, Garesse R, Arenas J, Martín MA. Association of novel POLG mutations and multiple mitochondrial DNA deletions with variable clinical phenotypes in a Spanish population. Arch Neurol. 2006;63:107–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

