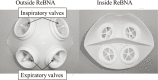
Effects of combined training with breathing resistance and sustained physical exertion to improve endurance capacity and respiratory muscle function in healthy young adults
- PMID: 24259812
- PMCID: PMC3804987
- DOI: 10.1589/jpts.25.605
Effects of combined training with breathing resistance and sustained physical exertion to improve endurance capacity and respiratory muscle function in healthy young adults
Abstract
[Purpose] In this study, combined training with breathing resistance and sustained physical exertion was carried out to evaluate its physiological effects and its effect on improve endurance capacity. [Subjects and Methods] The subjects were nine healthy adults (mean age 20.4, SD ± 1.7 years). The combined training group (n = 5) carried out 6 weeks of combined training using a cycle ergometer, with exercise load tests and respiratory function tests performed before and after the training. The results of the training were compared to a control group (n = 4) that only performed the cycling exercise without the combined training with breathing resistance. [Results] In the combined training group, ventilatory threshold, maximal load of the cycle ergometer in exercise load tests, and maximal voluntary ventilation increased after training. These increases after training were all significant, but none of these variables changed significantly in the control group. [Conclusion] The results imply that in comparison to conventional training methods, combined training with breathing resistance and sustained physical exertion is beneficial for increasing endurance capacity and respiratory muscle function. This result provides important information regarding the effects of the new training method for improving endurance capacity.
Keywords: Cardiorespiratory endurance; Exercise tolerance; Respiratory muscle training.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Respiratory muscle endurance training: effect on normoxic and hypoxic exercise performance.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010 Mar;108(4):759-69. doi: 10.1007/s00421-009-1286-0. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20187281 Clinical Trial.
-
Benefit of selective respiratory muscle training on exercise capacity in patients with chronic congestive heart failure.Circulation. 1995 Jan 15;91(2):320-9. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.2.320. Circulation. 1995. PMID: 7805234
-
Inspiratory muscle training reduces diaphragm activation and dyspnea during exercise in COPD.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018 Aug 1;125(2):381-392. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01078.2017. Epub 2018 Mar 15. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018. PMID: 29543134 Clinical Trial.
-
Putative Role of Respiratory Muscle Training to Improve Endurance Performance in Hypoxia: A Review.Front Physiol. 2019 Jan 15;9:1970. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01970. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30697170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Respiratory muscle training for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Phys Ther. 1995 Nov;75(11):996-1005. doi: 10.1093/ptj/75.11.996. Phys Ther. 1995. PMID: 7480129 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Wearing the Elevation Training Mask on Aerobic Capacity, Lung Function, and Hematological Variables.J Sports Sci Med. 2016 May 23;15(2):379-86. eCollection 2016 Jun. J Sports Sci Med. 2016. PMID: 27274679 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of complete decongestive therapy and a home program for patients with post mastectomy lymphedema.J Phys Ther Sci. 2015 Sep;27(9):2743-8. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.2743. Epub 2015 Sep 30. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015. PMID: 26504284 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of a Six-Week Swimming Training with Added Respiratory Dead Space on Respiratory Muscle Strength and Pulmonary Function in Recreational Swimmers.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Aug 8;17(16):5743. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17165743. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32784446 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of chest resistance exercise and chest expansion exercise on stroke patients' respiratory function and trunk control ability.J Phys Ther Sci. 2015 Jun;27(6):1655-8. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.1655. Epub 2015 Jun 30. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015. PMID: 26180292 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of chest expansion resistance exercise on chest expansion and maximal respiratory pressure in elderly with inspiratory muscle weakness.J Phys Ther Sci. 2015 Apr;27(4):1121-4. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.1121. Epub 2015 Apr 30. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015. PMID: 25995570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanaka K, Matsuura Y, Kumagai S, et al. : Relationships of anaerobic threshold and onset of blood lactate accumulation with endurance performance. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol, 1983, 52: 51–56 - PubMed
-
- Tanaka K, Watanabe H, Konishi Y, et al. : Longitudinal associations between anaerobic threshold and distance running performance. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol, 1986, 55: 248–252 - PubMed
-
- Medicine ACoS: ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. New York: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2011
-
- Sesso HD, Paffenbarger RS, Jr, Lee IM: Physical activity and coronary heart disease in men: the Harvard Alumni Health Study. Circulation, 2000, 102: 975–980 - PubMed
-
- Blair SN, Kohl HW, 3rd, Paffenbarger RS, Jr, et al. : Physical fitness and all-cause mortality. A prospective study of healthy men and women. JAMA, 1989, 262: 2395–2401 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources