Morphological and functional evaluation of chronic pancreatitis with magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 24259954
- PMCID: PMC3831205
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7241
Morphological and functional evaluation of chronic pancreatitis with magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
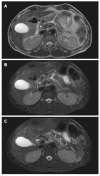
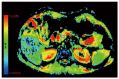
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques for assessment of morphology and function of the pancreas have been improved dramatically the recent years and MRI is very often used in diagnosing and follow-up of chronic pancreatitis (CP) patients. Standard MRI including fat-suppressed T1-weighted and T2-weighted imaging techniques reveal decreased signal and glandular atrophy of the pancreas in CP. In contrast-enhanced MRI of the pancreas in CP the pancreatic signal is usually reduced and delayed due to decreased perfusion as a result of chronic inflammation and fibrosis. Thus, morphological changes of the ductal system can be assessed by magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). Furthermore, secretin-stimulated MRCP is a valuable technique to evaluate side branch pathology and the exocrine function of the pancreas and diffusion weighted imaging can be used to quantify both parenchymal fibrotic changes and the exocrine function of the pancreas. These standard and advanced MRI techniques are supplementary techniques to reveal morphological and functional changes of the pancreas in CP. Recently, spectroscopy has been used for assessment of metabolite concentrations in-vivo in different tissues and may have the potential to offer better tissue characterization of the pancreas. Hence, the purpose of the present review is to provide an update on standard and advanced MRI techniques of the pancreas in CP.
Keywords: Chronic pancreatitis; Diffusion weighted imaging; Exocrine pancreatic function; Magnetic resonance; Secretin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Performance of Contrast-Enhanced MRI With Secretin-Stimulated MRCP for Non-Calcific Chronic Pancreatitis: A Comparison With Histopathology.Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov;110(11):1598-606. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2015.297. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26372506
-
MRI assessment of chronic pancreatitis.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2011 Sep;17(3):249-54. doi: 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3889-10.0. Epub 2010 Nov 14. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2011. PMID: 20945291 Review.
-
Quantification of pancreatic exocrine function of chronic pancreatitis with secretin-enhanced MRCP.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Nov 7;19(41):7177-82. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i41.7177. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24222963 Free PMC article.
-
Normal pancreatic exocrine function does not exclude MRI/MRCP chronic pancreatitis findings.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008 Sep;42(8):950-5. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31812f4ef5. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18645530
-
Diagnosis of early-stage chronic pancreatitis by secretin-enhanced magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jan;42 Suppl 17:113-7. doi: 10.1007/s00535-006-1919-6. J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17238039 Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatitis in Children.Gastroenterology. 2019 May;156(7):1969-1978. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.12.043. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30716320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging of pancreatitis: an update.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 28;20(40):14760-77. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14760. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25356038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Performance of Contrast-Enhanced MRI With Secretin-Stimulated MRCP for Non-Calcific Chronic Pancreatitis: A Comparison With Histopathology.Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov;110(11):1598-606. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2015.297. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26372506
-
Quantitative pancreatic MRI: a pathology-based review.Br J Radiol. 2019 Jul;92(1099):20180941. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180941. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Br J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30982337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anatomic variations of the pancreatic duct and their relevance with the Cambridge classification system: MRCP findings of 1158 consecutive patients.Radiol Oncol. 2016 Sep 8;50(4):370-377. doi: 10.1515/raon-2016-0041. eCollection 2016 Dec 1. Radiol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27904444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Layer P, Yamamoto H, Kalthoff L, Clain JE, Bakken LJ, DiMagno EP. The different courses of early- and late-onset idiopathic and alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1994;107:1481–1487. - PubMed
-
- Semelka RC, Kroeker MA, Shoenut JP, Kroeker R, Yaffe CS, Micflikier AB. Pancreatic disease: prospective comparison of CT, ERCP, and 1.5-T MR imaging with dynamic gadolinium enhancement and fat suppression. Radiology. 1991;181:785–791. - PubMed
-
- Semelka RC, Shoenut JP, Kroeker MA, Micflikier AB. Chronic pancreatitis: MR imaging features before and after administration of gadopentetate dimeglumine. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1993;3:79–82. - PubMed
-
- Sica GT, Miller FH, Rodriguez G, McTavish J, Banks PA. Magnetic resonance imaging in patients with pancreatitis: evaluation of signal intensity and enhancement changes. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;15:275–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

