Prevention of postpartum hemorrhage in low-resource settings: current perspectives
- PMID: 24259988
- PMCID: PMC3833941
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S51661
Prevention of postpartum hemorrhage in low-resource settings: current perspectives
Abstract
Background: Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is the leading cause of maternal death in low-income countries and is the primary cause of approximately one-quarter of global maternal deaths. The purpose of this paper is to provide a review of PPH prevention interventions, with a particular focus on misoprostol, and the challenges and opportunities that preventing PPH in low-resource settings presents.
Methods: Using PubMed, we conducted a review of the literature on the randomized controlled trials of interventions to prevent PPH. We then searched PubMed and Google Scholar for nonrandomized field trials of interventions to prevent PPH. We limited our review to interventions that are discussed in the current World Health Organization (WHO) recommendations for PPH prevention and present evidence regarding the use of these interventions. We focused our review on nondrug PPH prevention interventions compared with no intervention and uterotonics versus placebo; this review does not decipher the relative effectiveness of uterotonic drugs. We describe challenges to and opportunities for scaling up PPH prevention interventions.
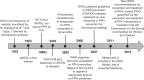
Results: Active management of the third stage of labor is considered the "gold standard" strategy for reducing the incidence of PPH. It combines nondrug interventions (controlled cord traction and cord clamping) with the administration of an uterotonic drug, the preferred uterotonic being oxytocin. Unfortunately, oxytocin has limited application in resource-poor countries, due to its heat instability and required administration by a skilled provider. New heat-stable drugs and drug formulations are currently in development that may improve the prevention of PPH; however, misoprostol is a viable option for provision at home by a lay health care worker or the woman herself, in the interim.
Conclusion: As the main cause of maternal mortality worldwide, PPH prevention interventions need to be prioritized. Increased access to prophylactic uterotonics, regardless of where deliveries occur, should be the primary means of reducing the burden of this complication.
Keywords: AMTSL; PPH prevention; misoprostol; oxytocin; uterotonics.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Reducing the global burden: postpartum haemorrhage. Making Pregnancy Safer. 2007;1(4):8.
-
- AbouZahr C. Global burden of maternal death and disability. Br Med Bull. 2003;67:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Dept of Reproductive Health and research, World Health Organization (WHO) WHO Recommendations for the Prevention and Treatment of Postpartum Haemorrhage. Geneva: WHO; 2012. - PubMed
-
- Abalos E.Choice of uterotonic agents in the active management of the third stage of labour: RHL commentary [webpage on the Internet] Geneva: WHO Reproductive Health Library; 2009[updated March 2, 2009]. Available from: http://apps.who.int/rhl/pregnancy_childbirth/childbirth/3rd_stage/cd0002...Accessed September 1, 2013
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

