Prognostic value of Annexin A3 in human colorectal cancer and its correlation with hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- PMID: 24260057
- PMCID: PMC3834359
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2013.1620
Prognostic value of Annexin A3 in human colorectal cancer and its correlation with hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
Abstract
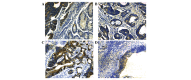
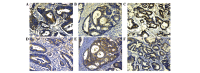
Annexins are a family of intracellular proteins that bind membrane phospholipids in a Ca2+ concentration-dependent manner and are involved in cellular processes, including apoptosis, proliferation and differentiation. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) has been hypothesized to be critical in the angiogenesis of tumors. We hypothesized that Annexin A3, a member of the Annexin family, and HIF-1α may be associated with each other in colorectal cancer. The expression of Annexin A3 and HIF-1α in 60 colorectal cancer tissues was assessed by immunohistochemistry to statistically analyze the association between the clinicopathological features and survival of these cases. In the present study, 65 and 47% of colorectal cancer specimens were found to show Annexin A3 and HIF-1α immunoreactivity, respectively. Annexin A3 expression was found to significantly correlate with tumor size and Dukes' stage (all P<0.05). Furthermore, Annexin A3 and HIF-1α protein expression exhibited a similar pattern in these samples, and their expression was found to correlate with poor survival in colorectal cancer patients. The results of the current study indicated for the first time that the increased expression of Annexin A3 in colorectal cancer correlates significantly with tumor growth and poor prognosis. Furthermore, Annexin A3 has been found to correlate with HIF-1α expression. These observations highlight an improved understanding of the carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer.
Keywords: Annexin A3; colorectal cancer; hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; immunohistochemistry; prognosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of HIF-1α, ANXA3, CD133 and their associations with clinicopathological parameters in human colon carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Jun;11(6):1644-1651. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-1277. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35836510 Free PMC article.
-
Annexin A3 is associated with a poor prognosis in breast cancer and participates in the modulation of apoptosis in vitro by affecting the Bcl-2/Bax balance.Exp Mol Pathol. 2013 Aug;95(1):23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Exp Mol Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23631820
-
Expression and significance of PTEN, hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in colorectal adenoma and adenocarcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Mar;9(3):491-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i3.491. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12632503 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation and stabilization of HIF-1alpha in colorectal carcinomas.Surg Oncol. 2007 Dec;16 Suppl 1:S25-7. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2007.10.014. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Surg Oncol. 2007. PMID: 18023174 Review.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic value of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in patients with bone tumor: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2019 Feb 19;14(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1101-5. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 30782196 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of HIF-1α in digestive system malignancies: evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2022 Spring;15(2):108-119. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2022. PMID: 35845307 Free PMC article.
-
Global Proteomic Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Human Embryonic Stem Cells via Connective Tissue Growth Factor Treatment under Chemically Defined Feeder-Free Culture Conditions.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jan 28;32(1):126-140. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2110.10032. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34750284 Free PMC article.
-
Carcinoma cells that have undergone an epithelial-mesenchymal transition differentiate into endothelial cells and contribute to tumor growth.Oncotarget. 2021 Apr 13;12(8):823-844. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27940. eCollection 2021 Apr 13. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 33889304 Free PMC article.
-
Annexin A3 and cancer.Oncol Lett. 2021 Dec;22(6):834. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13095. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34712358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of annexin A3 in breast cancer (Review).Mol Clin Oncol. 2022 Jun;16(6):111. doi: 10.3892/mco.2022.2544. Epub 2022 May 12. Mol Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35620213 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saif MW. Targeted agents for adjuvant therapy of colon cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2006;6:46–51. - PubMed
-
- Raynal P, Pollard HB. Annexins: the problem of assessing the biological role for a gene family of multifunctional calcium- and phospholipid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1197:63–93. - PubMed
-
- Gerke V, Moss SE. Annexins: from structure to function. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:331–371. - PubMed
-
- Gerke V, Creutz CE, Moss SE. Annexins: linking Ca2+ signalling to membrane dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:449–461. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
