DNA, cell wall and general oxidative damage underlie the tellurite/cefotaxime synergistic effect in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 24260236
- PMCID: PMC3832599
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079499
DNA, cell wall and general oxidative damage underlie the tellurite/cefotaxime synergistic effect in Escherichia coli
Abstract
The constant emergence of antibiotic multi-resistant pathogens is a concern worldwide. An alternative for bacterial treatment using nM concentrations of tellurite was recently proposed to boost antibiotic-toxicity and a synergistic effect of tellurite/cefotaxime (CTX) was described. In this work, the molecular mechanism underlying this phenomenon is proposed. Global changes of the transcriptional profile of Escherichia coli exposed to tellurite/CTX were determined by DNA microarrays. Induction of a number of stress regulators (as SoxS), genes related to oxidative damage and membrane transporters was observed. Accordingly, increased tellurite adsorption/uptake and oxidative injuries to proteins and DNA were determined in cells exposed to the mixture of toxicants, suggesting that the tellurite-mediated CTX-potentiating effect is dependent, at least in part, on oxidative stress. Thus, the synergistic tellurite-mediated CTX-potentiating effect depends on increased tellurite uptake/adsorption which results in damage to proteins, DNA and probably other macromolecules. Our findings represent a contribution to the current knowledge of bacterial physiology under antibiotic stress and can be of great interest in the development of new antibiotic-potentiating strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


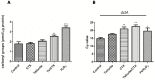
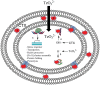
References
-
- Walsh C (2003) Where will new antibiotics come from? Nat Rev Microbiol 1: 65–70. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell G, Lafrance M, Boulanger S, Séguin DL, Guay I, et al. (2012) Tomatidine acts in synergy with aminoglycoside antibiotics against multiresistant Staphylococcus aureus and prevents virulence gene expression. J Antimicrob Chemother 67: 559–568. - PubMed
-
- Halwani M, Hebert S, Suntres ZE, Lafrenie RM, Azghani AO, et al. (2009) Bismuth-thiol incorporation enhances biological activities of liposomal tobramycin against bacterial biofilm and quorum sensing molecules production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Int J Pharm 373: 141–146. - PubMed
-
- Kohanski MD, Dwyer D, Hayete B, Lawrence C, Collins J (2007) A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell 130: 797–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

