Combination of cytokine responses indicative of latent TB and active TB in Malawian adults
- PMID: 24260295
- PMCID: PMC3832606
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079742
Combination of cytokine responses indicative of latent TB and active TB in Malawian adults
Abstract
Background: An IFN-γ response to M. tuberculosis-specific antigens is an effective biomarker for M. tuberculosis infection but it cannot discriminate between latent TB infection and active TB disease. Combining a number of cytokine/chemokine responses to M. tuberculosis antigens may enable differentiation of latent TB from active disease.
Methods: Asymptomatic recently-exposed individuals (spouses of TB patients) were recruited and tuberculin skin tested, bled and followed-up for two years. Culture supernatants, from a six-day culture of diluted whole blood samples stimulated with M. tuberculosis-derived PPD or ESAT-6, were measured for IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-13, IL-17, TNF-α and CXCL10 using cytokine ELISAs. In addition, 15 patients with sputum smear-positive pulmonary TB were recruited and tested.
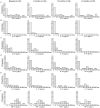
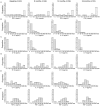
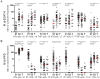
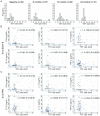
Results: Spouses with positive IFN-γ responses to M. tuberculosis ESAT-6 (>62.5 pg/mL) and TB patients showed high production of IL-17, CXCL10 and TNF-α. Higher production of IL-10 and IL-17 in response to ESAT-6 was observed in the spouses compared with TB patients while the ratios of IFN-γ/IL-10 and IFN-γ/IL-17 in response to M. tuberculosis-derived PPD were significantly higher in TB patients compared with the spouses. Tuberculin skin test results did not correlate with cytokine responses.
Conclusions: CXCL10 and TNF-α may be used as adjunct markers alongside an IFN-γ release assay to diagnose M. tuberculosis infection, and IL-17 and IL-10 production may differentiate individuals with LTBI from active TB.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- WHO (2011) Global Tuberculosis Control 2011. Available: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/2011/gtbr11_full.pdf. Accessed 25 January 2013.
-
- Onyebujoh P, Rook GA (2004) Tuberculosis. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(12): 930–932. - PubMed
-
- Pai M, Riley LW, Colford JM (2004) Interferon-γ assays in the immunodiagnosis of tuberculosis: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis 4: 761–776. - PubMed
-
- Claessens NJ, Gausi FF, Meijnen S, Weismuller MM, Salaniponi FM, et al. (2002) High frequency of tuberculosis in households of index TB patients. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 6(3): 266–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

