Analysis and optimization of bulk DNA sampling with binary scoring for germplasm characterization
- PMID: 24260321
- PMCID: PMC3833943
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079936
Analysis and optimization of bulk DNA sampling with binary scoring for germplasm characterization
Abstract
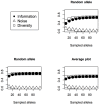
The strategy of bulk DNA sampling has been a valuable method for studying large numbers of individuals through genetic markers. The application of this strategy for discrimination among germplasm sources was analyzed through information theory, considering the case of polymorphic alleles scored binarily for their presence or absence in DNA pools. We defined the informativeness of a set of marker loci in bulks as the mutual information between genotype and population identity, composed by two terms: diversity and noise. The first term is the entropy of bulk genotypes, whereas the noise term is measured through the conditional entropy of bulk genotypes given germplasm sources. Thus, optimizing marker information implies increasing diversity and reducing noise. Simple formulas were devised to estimate marker information per allele from a set of estimated allele frequencies across populations. As an example, they allowed optimization of bulk size for SSR genotyping in maize, from allele frequencies estimated in a sample of 56 maize populations. It was found that a sample of 30 plants from a random mating population is adequate for maize germplasm SSR characterization. We analyzed the use of divided bulks to overcome the allele dilution problem in DNA pools, and concluded that samples of 30 plants divided into three bulks of 10 plants are efficient to characterize maize germplasm sources through SSR with a good control of the dilution problem. We estimated the informativeness of 30 SSR loci from the estimated allele frequencies in maize populations, and found a wide variation of marker informativeness, which positively correlated with the number of alleles per locus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Deputy J, Ming R, Ma H, Liu Z, Fitch M, et al. (2002) Molecular markers for sex determination in papaya (Carica papaya L.). Theor Appl Genet 106: 107–111. - PubMed
-
- Martinez E, Destombe C, Quillet M, Valero M (1999) Identification of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers highly linked to sex determination in the red alga Gracilaria gracilis . Mol Ecol 8: 1533–1538. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

