Neurosteroid 3α-androstanediol efficiently counteracts paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy and painful symptoms
- PMID: 24260511
- PMCID: PMC3829913
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080915
Neurosteroid 3α-androstanediol efficiently counteracts paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy and painful symptoms
Abstract
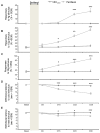
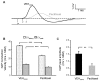
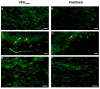
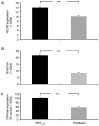
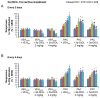
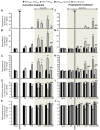
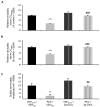
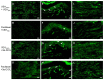
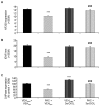
Painful peripheral neuropathy belongs to major side-effects limiting cancer chemotherapy. Paclitaxel, widely used to treat several cancers, induces neurological symptoms including burning pain, allodynia, hyperalgesia and numbness. Therefore, identification of drugs that may effectively counteract paclitaxel-induced neuropathic symptoms is crucial. Here, we combined histopathological, neurochemical, behavioral and electrophysiological methods to investigate the natural neurosteroid 3α-androstanediol (3α-DIOL) ability to counteract paclitaxel-evoked peripheral nerve tissue damages and neurological symptoms. Prophylactic or corrective 3α-DIOL treatment (4 mg/kg/2 days) prevented or suppressed PAC-evoked heat-thermal hyperalgesia, cold-allodynia and mechanical allodynia/hyperalgesia, by reversing to normal, decreased thermal and mechanical pain thresholds of PAC-treated rats. Electrophysiological studies demonstrated that 3α-DIOL restored control values of nerve conduction velocity and action potential peak amplitude significantly altered by PAC-treatment. 3α-DIOL also repaired PAC-induced nerve damages by restoring normal neurofilament-200 level in peripheral axons and control amount of 2',3'-cyclic-nucleotide-3'-phosphodiesterase in myelin sheaths. Decreased density of intraepidermal nerve fibers evoked by PAC-therapy was also counteracted by 3α-DIOL treatment. More importantly, 3α-DIOL beneficial effects were not sedation-dependent but resulted from its neuroprotective ability, nerve tissue repairing capacity and long-term analgesic action. Altogether, our results showing that 3α-DIOL efficiently counteracted PAC-evoked painful symptoms, also offer interesting possibilities to develop neurosteroid-based strategies against chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. This article shows that the prophylactic or corrective treatment with 3α-androstanediol prevents or suppresses PAC-evoked painful symptoms and peripheral nerve dysfunctions in rats. The data suggest that 3α-androstanediol-based therapy may constitute an efficient strategy to explore in humans for the eradication of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

