Serum concentrations of fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: association with insulin resistance, adiponectin, and polycystic ovary syndrome history
- PMID: 24260557
- PMCID: PMC3834317
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081190
Serum concentrations of fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: association with insulin resistance, adiponectin, and polycystic ovary syndrome history
Abstract
Background: Fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) and FGF21 are considered to be novel adipokines that improve glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. In the current study, we investigated serum FGF19 and FGF21 levels in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and explored their relationships with anthropometric and endocrine parameters.
Method: Serum FGF19 and FGF21 levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in patients with GDM (n = 30) and healthy pregnant controls (n = 60) matched for maternal and gestational age. Serum FGF19 and FGF21 levels were correlated with anthropometric, metabolic, and endocrine parameters.
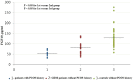
Results: Circulating levels of FGF19 were significantly reduced in patients with GDM relative to healthy pregnant subjects, whereas FGF21 levels were increased in GDM patients. Serum FGF19 levels independently and inversely correlated with insulin resistance (increased homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, HOMA-IR) and were positively related to serum adiponectin in both groups. In contrast, serum FGF21 levels independently and positively correlated with insulin resistance and serum triglycerides and were inversely related to serum adiponectin. In addition, in the combined population of both groups, those women with preconception polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) history had the lowest levels of FGF19, which were significantly lower than those in GDM patients without PCOS history and those in controls without PCOS history.
Conclusions: Circulating FGF19 levels are reduced in GDM patients, in contrast with FGF21 levels. Both serum FGF19 and FGF21 levels are strongly related to insulin resistance and serum levels of adiponectin. Considering the different situation between FGF19 and FGF21, we suggest that reduced serum FGF19 levels could be involved in the pathophysiology of GDM, while increased serum FGF21 levels could be in a compensatory response to this disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elevated plasma SPARC levels are associated with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and inflammation in gestational diabetes mellitus.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 9;8(12):e81615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081615. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349098 Free PMC article.
-
Serum fibroblast growth factor 21 levels in gestational diabetes mellitus in relation to insulin resistance and dyslipidemia.Metabolism. 2010 Jan;59(1):33-7. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.07.003. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Metabolism. 2010. PMID: 19699495
-
Lower cerebrospinal fluid/plasma fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) ratios and placental FGF21 production in gestational diabetes.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 3;8(6):e65254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065254. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23755203 Free PMC article.
-
Role of fibroblast growth factor 21 in gestational diabetes mellitus: A mini-review.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2019 Jan;90(1):47-55. doi: 10.1111/cen.13881. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2019. PMID: 30346647 Review.
-
The Role of the FGF19 Family in the Pathogenesis of Gestational Diabetes: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 9;24(24):17298. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417298. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139126 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Value of Bile Acids and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.Womens Health Rep (New Rochelle). 2022 Sep 26;3(1):803-812. doi: 10.1089/whr.2022.0060. eCollection 2022. Womens Health Rep (New Rochelle). 2022. PMID: 36204478 Free PMC article.
-
Serum fibroblast growth factor 19 is decreased in patients with overt hypothyroidism and subclinical hypothyroidism.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Sep;95(39):e5001. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005001. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27684859 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Diabetes Res. 2023 Oct 14;2023:4024877. doi: 10.1155/2023/4024877. eCollection 2023. J Diabetes Res. 2023. PMID: 37869250 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of pregnancy disorder in the first-trimester patient plasma with Raman spectroscopy and protein analysis.Bioeng Transl Med. 2024 Jul 16;9(6):e10691. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10691. eCollection 2024 Nov. Bioeng Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39545096 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin, A-FABP and FGF-19 Levels in Women with Early Diagnosed Gestational Diabetes.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 25;11(9):2417. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092417. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35566542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes-Powell LL (2007) Infants of diabetic mothers: the effects of hyperglycemia on the fetus and neonate. Neonatal Netw 26: 283–290. - PubMed
-
- Bo S, Valpreda S, Menato G, Bardelli C, Botto C, et al. (2007) Should we consider gestational diabetes a vascular risk factor? Atherosclerosis 194: e72–e79. - PubMed
-
- Bellamy L, Casas JP, Hingorani AD, Williams D (2009) Type 2 diabetes mellitus after gestational diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 373: 1773–1779. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

