Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors as cancer therapeutics
- PMID: 24261963
- PMCID: PMC3843585
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-88
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors as cancer therapeutics
Abstract
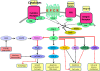
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3Ks) are lipid kinases that regulate diverse cellular processes including proliferation, adhesion, survival, and motility. Dysregulated PI3K pathway signaling occurs in one-third of human tumors. Aberrantly activated PI3K signaling also confers sensitivity and resistance to conventional therapies. PI3K has been recognized as an attractive molecular target for novel anti-cancer molecules. In the last few years, several classes of potent and selective small molecule PI3K inhibitors have been developed, and at least fifteen compounds have progressed into clinical trials as new anticancer drugs. Among these, idelalisib has advanced to phase III trials in patients with advanced indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma. In this review, we summarized the major molecules of PI3K signaling pathway, and discussed the preclinical models and clinical trials of potent small-molecule PI3K inhibitors.
Figures


References
-
- Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002;296(5573):1655–1657. - PubMed
-
- Burris HA 3rd. Overcoming acquired resistance to anticancer therapy: focus on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013;71(4):829–842. - PubMed
-
- Osaki M, Oshimura M, Ito H. PI3K-Akt pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis. 2004;9(6):667–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

