N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane sensitizes bladder cancer cells to doxorubicin by preventing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 activation
- PMID: 24262005
- PMCID: PMC4317814
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12328
N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane sensitizes bladder cancer cells to doxorubicin by preventing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 activation
Abstract
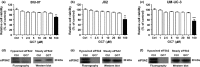
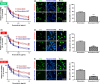
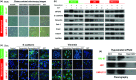
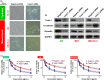
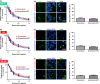
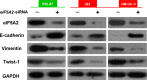
Drug resistance greatly reduces the efficacy of doxorubicin-based chemotherapy in bladder cancer treatment; however, the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. We aimed to investigate whether N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane (GC7), which inhibits eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2) activation, exerts synergistic cytotoxicity with doxorubicin in bladder cancer, and whether eIF5A2 is involved in chemoresistance to doxorubicin-based bladder cancer treatment. BIU-87, J82, and UM-UC-3 bladder cancer cells were transfected with eIF5A2 siRNA or negative control siRNA before incubation with doxorubicin alone or doxorubicin plus GC7 for 48 h. Doxorubicin cytotoxicity was enhanced by GC7 in BIU-87, J82, and UM-UC-3 cells. It significantly inhibited activity of eIF5A2, suppressed doxorubicin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in BIU-87 cells, and promoted mesenchymal-epithelial transition in J82 and UM-UC-3 cells. Knockdown of eIF5A2 sensitized bladder cancer cells to doxorubicin, prevented doxorubicin-induced EMT in BIU-87 cells, and encouraged mesenchymal-epithelial transition in J82 and UM-UC-3 cells. Combination therapy with GC7 may enhance the therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin in bladder cancer by inhibiting eIF5A2 activation and preventing epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Keywords: Doxorubicin; drug resistance; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A; urinary bladder neoplasms.
© 2013 The Authors. Cancer Science published by Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane (GC7) enhances the therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin by inhibiting activation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2) and preventing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Exp Cell Res. 2013 Oct 15;319(17):2708-17. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.08.010. Epub 2013 Aug 16. Exp Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23958463
-
N1-Guanyl-1,7-Diaminoheptane Sensitizes Estrogen Receptor Negative Breast Cancer Cells to Doxorubicin by Preventing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through Inhibition of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 5A2 Activation.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(6):2494-503. doi: 10.1159/000430209. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26279450
-
GC7 enhances cisplatin sensitivity via STAT3 signaling pathway inhibition and eIF5A2 inactivation in mesenchymal phenotype oral cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2018 Mar;39(3):1283-1291. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.6161. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29286162
-
Roles of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 in human cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2013 Oct 12;9(10):1013-20. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7191. eCollection 2013. Int J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24250246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling EIF5A2: A multifaceted player in cellular regulation, tumorigenesis and drug resistance.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 15;997:177596. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177596. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40194645 Review.
Cited by
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A in the pathogenesis of cancers.Oncol Lett. 2020 Oct;20(4):81. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11942. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32863914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LSD1 Promotes Bladder Cancer Progression by Upregulating LEF1 and Enhancing EMT.Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 28;10:1234. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01234. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32850370 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of EIF5A2 induces tumor vasculature remodeling and improves tumor response to chemotherapy via regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 expression.Oncotarget. 2014 Aug 30;5(16):6716-33. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2236. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25071013 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting eIF5A2 reduces invasion and reverses chemoresistance in SCC-9 cells in vitro.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Apr;39(4):463-470. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-637. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 37334930
-
Stemness and chemotherapeutic drug resistance induced by EIF5A2 overexpression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 22;6(28):26079-89. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4581. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26317793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grimm MO, Steinhoff C, Simon X, Spiegelhalder P, Ackermann R, Vogeli TA. Effect of routine repeat transurethral resection for superficial bladder cancer: a long-term observational study. J Urol. 2003;170:433–7. - PubMed
-
- Chang SS, Alberts G, Cookson MS, Smith JA., Jr Radical cystectomy is safe in elderly patients at high risk. J Urol. 2001;166:938–41. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi A, Shiota M, Tatsugami K, et al. p300 mediates cellular resistance to doxorubicin in bladder cancer. Mol Med Rep. 2012;5:173–6. - PubMed
-
- Gan Y, Wientjes MG, Badalament RA, Au JL. Pharmacodynamics of doxorubicin in human bladder tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 1996;2:1275–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

