Dual inhibition of PI3K and mTOR signaling pathways decreases human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor metastatic progression
- PMID: 24263107
- PMCID: PMC3864633
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182a44ab4
Dual inhibition of PI3K and mTOR signaling pathways decreases human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor metastatic progression
Abstract
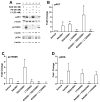
Objectives: Patients with advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors have limited therapeutic options. Everolimus (RAD001), an inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway, has been shown to increase progression-free survival, but not overall survival, indicating a need to identify additional therapeutic targets. Inhibition of mTOR complex 1 by RAD001 may induce upstream AKT upregulation. We hypothesized that dual inhibition of AKT along with mTOR will overcome the limited activity of RAD001 alone.
Methods: The BON cell line has been used as a model to study pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor cell biology. Western blots and cell growth assays were performed with mTOR inhibitor RAD001 (50 nM), mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor PD0325901 (50 nM), PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase) inhibitor LY294002 (25 μM), or vehicle control. Nude mice were treated daily for 6 weeks with RAD001 (oral gavage) and with LY29400 (subcutaneous) 1 week after intrasplenic injection of BON cells.
Results: Cellular proliferation was most attenuated with the combination therapy of LY29400 and RAD001. Similarly, the volume of liver metastasis was lowest in the group treated with both LY29400 (100 mg/kg per week, subcutaneous) and RAD001 (2.5 mg/kg per day) compared with that in the vehicle group (P = 0.04).
Conclusion: The combination therapy of LY29400 and RAD001 decreased the cell growth in vitro and progression of liver metastasis in vivo compared with vehicle or with single-drug therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Conflicts of Interest and Source of Funding: This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (T32-DK007639 to MRH and K08-CA125209 to CC).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combined therapy with RAD001 e BEZ235 overcomes resistance of PET immortalized cell lines to mTOR inhibition.Oncotarget. 2014 Jul 30;5(14):5381-91. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2111. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25026292 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of dual mTORC1/2 mTOR kinase inhibitor AZD8055 on acquired endocrine resistance in breast cancer in vitro.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Jan 23;16(1):R12. doi: 10.1186/bcr3604. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24457069 Free PMC article.
-
Combined targeting of AKT and mTOR synergistically inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Mol Cancer. 2012 Nov 20;11:85. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-85. Mol Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23167739 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors in the therapy of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.Cancer Lett. 2013 Jul 10;335(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.02.016. Epub 2013 Feb 16. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23419523 Review.
-
Targeting the mTOR signaling pathway in neuroendocrine tumors.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2014 Sep;15(3):365-79. doi: 10.1007/s11864-014-0294-4. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25092520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Translational Diagnostics and Therapeutics in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Oct 15;22(20):5022-5029. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0435. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27742788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel RICTOR amplification harbouring entities: FISH validation of RICTOR amplification in tumour tissue after next-generation sequencing.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 10;13(1):19610. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46927-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37949943 Free PMC article.
-
PAK4-NAMPT Dual Inhibition as a Novel Strategy for Therapy Resistant Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 29;11(12):1902. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121902. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31795447 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted therapy of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: preclinical strategies and future targets.Endocr Connect. 2018 Jan;7(1):R1-R25. doi: 10.1530/EC-17-0286. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Endocr Connect. 2018. PMID: 29146887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose‑derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate dibutyltin dichloride‑induced chronic pancreatitis by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Apr;21(4):1833-1840. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.10995. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32319628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yao JC, Hassan M, Phan A, et al. One hundred years after “carcinoid”: epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3063–3072. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Enewold L, Stojadinovic A, et al. Incidence rates of exocrine and endocrine pancreatic cancers in the United States. Cancer Causes Control. 2010;21:853–861. - PubMed
-
- Evers BM, Ishizuka J, Townsend CM, Jr, et al. The human carcinoid cell line, BON. A model system for the study of carcinoid tumors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994;733:393–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

