The Stress-response protein prostate-associated gene 4, interacts with c-Jun and potentiates its transactivation
- PMID: 24263171
- PMCID: PMC4086653
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.11.014
The Stress-response protein prostate-associated gene 4, interacts with c-Jun and potentiates its transactivation
Abstract
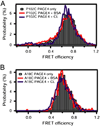
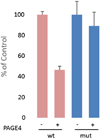
The Cancer/Testis Antigen (CTA), Prostate-associated Gene 4 (PAGE4), is a stress-response protein that is upregulated in prostate cancer (PCa) especially in precursor lesions that result from inflammatory stress. In cells under stress, translocation of PAGE4 to mitochondria increases while production of reactive oxygen species decreases. Furthermore, PAGE4 is also upregulated in human fetal prostate, underscoring its potential role in development. However, the proteins that interact with PAGE4 and the mechanisms underlying its pleiotropic functions in prostatic development and disease remain unknown. Here, we identified c-Jun as a PAGE4 interacting partner. We show that both PAGE4 and c-Jun are overexpressed in the human fetal prostate; and in cell-based assays, PAGE4 robustly potentiates c-Jun transactivation. Single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer experiments indicate that upon binding to c-Jun, PAGE4 undergoes conformational changes. However, no interaction is observed in presence of BSA or unilamellar vesicles containing the mitochondrial inner membrane diphosphatidylglycerol lipid marker cardiolipin. Together, our data indicate that PAGE4 specifically interacts with c-Jun and that, conformational dynamics may account for its observed pleiotropic functions. To our knowledge, this is the first report demonstrating crosstalk between a CTA and a proto-oncogene. Disrupting PAGE4/c-Jun interactions using small molecules may represent a novel therapeutic strategy for PCa.
Keywords: BPH; BSA; CD; Cancer/Testis Antigen; DBD; DLS; DMSO; DNA-binding domain; Dimethyl sulfoxide; IPTG; Intrinsically disordered protein; Isopropyl 1-thio-β-d-galactopyranoside; NMR; PAGE4; PBS; PC; PCa; PE; PIA; PIN; PINs; PVP; Phosphate Buffered Saline; Prostate Associated Gene 4; Prostate cancer; QY; SDS-PAGE; SEC; Sodium Dodecyl sulfate poly-acrylamide gel electrophoresis; TCEP·HCl; Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride; benign prostatic hyperplasia; bovine serum albumin; c-Jun; circular dichroism; dynamic light scattering; nuclear magnetic resonance; phosphatidylcholine; phosphatidylethanolamine; polyvinyl pyrollidone; proliferative inflammatory atrophy; prostate cancer; prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia; protein interaction networks; quantum yield; single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer; size exclusion chromatography; smFRET.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Simpson AJ, Caballero OL, Jungbluth A, Chen YT, Old LJ. Cancer/testis antigens, gametogenesis and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2005;5:615–625. - PubMed
-
- Scanlan MJ, Gure AO, Jungbluth AA, Old LJ, Chen YT. Cancer/testis antigens: an expanding family of targets for cancer immunotherapy. Immunol. Rev. 2002;188:22–32. - PubMed
-
- Sampson N, Ruiz C, Zenzmaier C, Bubendorf L, Berger P. PAGE4 positivity is associated with attenuated AR signaling and predicts patient survival in hormone-naive prostate cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2012;181:1443–1454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

