Novel molecular targets of dezocine and their clinical implications
- PMID: 24263237
- PMCID: PMC3944410
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000076
Novel molecular targets of dezocine and their clinical implications
Abstract
Background: Although dezocine is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist, it is not a controlled substance. Thus, the characterization of the molecular targets of dezocine is critical for scientific and clinical implications. The goal of this study is to characterize molecular targets for dezocine and determine their implications.
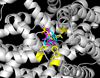
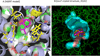
Methods: A binding screen for dezocine was performed on 44 available receptors and transporter proteins. Functional assays for the novel targets were performed along with computation calculations to locate the binding site. A G protein activation study was performed for the human κ opioid receptor to determine whether dezocine is a κ-antagonist. Data are presented as mean ± standard error.
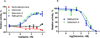
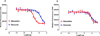
Results: The affinities for dezocine were 3.7 ± 0.7 nM for the μ receptor, 527 ± 70 nM for the δ-receptor, and 31.9 ± 1.9 nM for the κ-receptor. Dezocine failed to induce G protein activation with κ-opioid receptor and concentration dependently inhibited κ-agonist (salvinorin A and nalbuphine)-induced receptor activation, indicating that dezocine is a κ-antagonist. Two novel molecular targets (norepinephrine transporter and serotonin transporter) were identified. Dezocine concentration-dependently inhibited norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake in vitro. The half maximal inhibitory concentrations (expressed as pIC50) were 5.68 ± 0.11 for norepinephrine transporter and 5.86 ± 0.17 for serotonin transporter. Dezocine occupied the binding site for known norepinephrine transporter and serotonin transporter inhibitors.
Conclusions: The unique molecular pharmacological profile of dezocine as a partial μ-receptor agonist, a κ-receptor antagonist, and a norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibitor (via norepinephrine transporter and serotonin transporter) was revealed. These discoveries reveal potentially important novel clinical implications and drug interactions of dezocine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Fragen RJ, Caldwell N. Comparison of dezocine (WY 16, 225) and meperidine as postoperative analgesics. Anesth Analg. 1978;57:563–566. - PubMed
-
- Sun Q, Zhou W, Wu B, Ji MH, Peng YG. Dezocine: A novel drug to prevent fentanyl-induced cough during general anesthesia induction? J Anesth. 2012;26:470. - PubMed
-
- Gal TJ, DiFazio CA. Ventilatory and analgesic effects of dezocine in humans. Anesthesiology. 1984;61:716–722. - PubMed
-
- Mumby SM, Linder ME. Myristoylation of G-protein alpha subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1994;237:254–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

