Diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study at 30 years: advances and contributions
- PMID: 24264395
- PMCID: PMC3837056
- DOI: 10.2337/db13-1093
Diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study at 30 years: advances and contributions
Figures


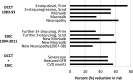
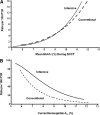
References
-
- The DCCT Research Group The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). Design and methodologic considerations for the feasibility phase. Diabetes 1986;35:530–545 - PubMed
-
- Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) Research Group Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC). Design, implementation, and preliminary results of a long-term follow-up of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial cohort. Diabetes Care 1999;22:99–111 - PMC - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977–986 - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM. Long-term complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;328:1676–1685 - PubMed
-
- Deckert T, Poulsen JE, Larsen M. Prognosis of diabetics with diabetes onset before the age of thirty-one. I. Survival, causes of death, and complications. Diabetologia 1978;14:363–370 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

