Nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical applications
- PMID: 24264728
- PMCID: PMC3924876
- DOI: 10.1002/bit.25160
Nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical applications
Abstract
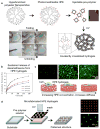
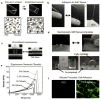
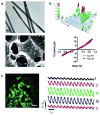
Hydrogels mimic native tissue microenvironment due to their porous and hydrated molecular structure. An emerging approach to reinforce polymeric hydrogels and to include multiple functionalities focuses on incorporating nanoparticles within the hydrogel network. A wide range of nanoparticles, such as carbon-based, polymeric, ceramic, and metallic nanomaterials can be integrated within the hydrogel networks to obtain nanocomposites with superior properties and tailored functionality. Nanocomposite hydrogels can be engineered to possess superior physical, chemical, electrical, and biological properties. This review focuses on the most recent developments in the field of nanocomposite hydrogels with emphasis on biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. In particular, we discuss synthesis and fabrication of nanocomposite hydrogels, examine their current limitations and conclude with future directions in designing more advanced nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical and biotechnological applications.
Keywords: biomedical applications; drug delivery; nanocomposite hydrogels; nanoparticles; tissue engineering.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Balazs AC, Emrick T, Russell TP. Nanoparticle polymer composites: Where two small worlds meet. Science. 2006;314(5802):1107–1110. - PubMed
-
- Bordes P, Pollet E, Avérous L. Nanobiocomposites: Biodegradable polyester/nanoclay systems. Prog Polym Sci. 2009;34(2):125–155.
-
- Caruso F. Nanoengineering of particle surfaces. Adv Mater. 2001;13(1):11–22.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

