MAP kinase pathway alterations in BRAF-mutant melanoma patients with acquired resistance to combined RAF/MEK inhibition
- PMID: 24265154
- PMCID: PMC3947296
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0631
MAP kinase pathway alterations in BRAF-mutant melanoma patients with acquired resistance to combined RAF/MEK inhibition
Abstract
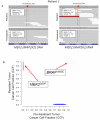
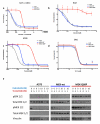
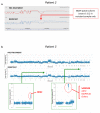
Treatment of BRAF-mutant melanoma with combined dabrafenib and trametinib, which target RAF and the downstream MAP-ERK kinase (MEK)1 and MEK2 kinases, respectively, improves progression-free survival and response rates compared with dabrafenib monotherapy. Mechanisms of clinical resistance to combined RAF/MEK inhibition are unknown. We performed whole-exome sequencing (WES) and whole-transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) on pretreatment and drug-resistant tumors from five patients with acquired resistance to dabrafenib/trametinib. In three of these patients, we identified additional mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway alterations in the resistant tumor that were not detected in the pretreatment tumor, including a novel activating mutation in MEK2 (MEK2(Q60P)). MEK2(Q60P) conferred resistance to combined RAF/MEK inhibition in vitro, but remained sensitive to inhibition of the downstream kinase extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). The continued MAPK signaling-based resistance identified in these patients suggests that alternative dosing of current agents, more potent RAF/MEK inhibitors, and/or inhibition of the downstream kinase ERK may be needed for durable control of BRAF-mutant melanoma.
Figures
Comment in
-
Therapeutics: delving deeper into resistance.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Jan;14(1):7. doi: 10.1038/nrc3653. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24505615 No abstract available.
References
-
- Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, Nathan P, Garbe C, Milhem M, et al. Improved survival with MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutated melanoma. The New England journal of medicine. 2012 Jul 12;367(2):107–14. PubMed PMID: 22663011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

