A molten globule intermediate of the von Willebrand factor A1 domain firmly tethers platelets under shear flow
- PMID: 24265179
- PMCID: PMC4006108
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.24464
A molten globule intermediate of the von Willebrand factor A1 domain firmly tethers platelets under shear flow
Abstract
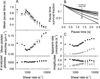
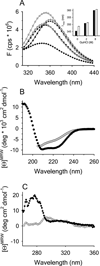
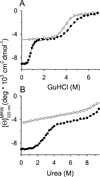
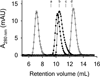
Clinical mutations in patients diagnosed with Type 2A von Willebrand disease (VWD) have been identified that break the single disulfide bond linking N- and C-termini in the vWF A1 domain. We have modeled the effect of these mutations on the disulfide-bonded structure of A1 by reducing and carboxy-amidating these cysteines. Solution biophysical studies show that loss of this disulfide bond induces a molten globule conformational state lacking global tertiary structure but retaining residual secondary structure. The conformational dependence of platelet adhesion to these native and molten globule states of A1 is quantitatively compared using real-time high-speed video microscopy analysis of platelet translocation dynamics under shear flow in a parallel plate microfluidic flow chamber. While normal platelets translocating on surface-captured native A1 domain retain the catch-bond character of pause times that increase as a function of shear rate at low shear and decrease as a function of shear rate at high shear, platelets that interact with A1 lacking the disulfide bond remain stably attached and do not translocate. Based on these findings, we propose that the shear stress-sensitive regulation of the A1-GPIb interaction is due to folding the tertiary structure of this domain. Removal of the tertiary structure by disrupting the disulfide bond destroys this regulatory mechanism resulting in high-strength interactions between platelets and vWF A1 that are dependent only on residual secondary structure elements present in the molten globule conformation.
Keywords: Von Willebrand disease type 2; Von Willebrand factor; disulfide bond; molten globule; platelet adhesiveness; protein folding; rheology; shear stress; thermodynamics.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Woods AI, Sanchez-Luceros A, Kempfer AC, et al. C1272F: a novel type 2A von Willebrand's disease mutation in A1 domain; its clinical significance. Haemophilia. 2012;18(1):112–116. - PubMed
-
- Penas N, Perez A, Gonzalez-Boullosa R, Batlle J. C1272S: a new candidate mutation in type 2A von Willebrand disease that disrupts the disulfide loop responsible for the interaction of VWF with platelet GP Ib-IX. Am J Hematol. 2004;75(2):73–77. - PubMed
-
- Meyer D, Fressinaud E, Gaucher C, et al. Gene defects in 150 unrelated French cases with type 2 von Willebrand disease: from the patient to the gene. INSERM Network on Molecular Abnormalities in von Willebrand Disease. Thromb. Haemost. 1997;78(1):451–456. - PubMed
-
- Lavergne JM, De Paillette L, Bahnak BR, et al. Defects in type IIA von Willebrand disease: a cysteine 509 to arginine substitution in the mature von Willebrand factor disrupts a disulphide loop involved in the interaction with platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX. Br J Haematol. 1992;82(1):66–72. - PubMed
-
- Azuma H, Hayashi T, Dent JA, Ruggeri ZM, Ware J. Disulfide bond requirements for assembly of the platelet glycoprotein Ib-binding domain of von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(4):2821–2827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

