Integrative functional genomic analyses implicate specific molecular pathways and circuits in autism
- PMID: 24267887
- PMCID: PMC3934107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.031
Integrative functional genomic analyses implicate specific molecular pathways and circuits in autism
Abstract
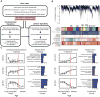
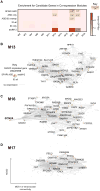
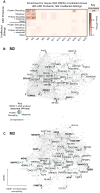
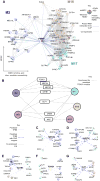
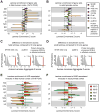
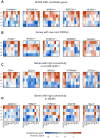
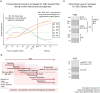
Genetic studies have identified dozens of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) susceptibility genes, raising two critical questions: (1) do these genetic loci converge on specific biological processes, and (2) where does the phenotypic specificity of ASD arise, given its genetic overlap with intellectual disability (ID)? To address this, we mapped ASD and ID risk genes onto coexpression networks representing developmental trajectories and transcriptional profiles representing fetal and adult cortical laminae. ASD genes tightly coalesce in modules that implicate distinct biological functions during human cortical development, including early transcriptional regulation and synaptic development. Bioinformatic analyses suggest that translational regulation by FMRP and transcriptional coregulation by common transcription factors connect these processes. At a circuit level, ASD genes are enriched in superficial cortical layers and glutamatergic projection neurons. Furthermore, we show that the patterns of ASD and ID risk genes are distinct, providing a biological framework for further investigating the pathophysiology of ASD.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH094714/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH073526/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32MH073526/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 9R01MH100027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS062691/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5R37MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01MH094714/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F30 MH099886/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F30MH099886/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH100027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30NS062691/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

