Bile acids activate YAP to promote liver carcinogenesis
- PMID: 24268772
- PMCID: PMC3961013
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.10.030
Bile acids activate YAP to promote liver carcinogenesis
Abstract
Elevated bile acid levels increase hepatocellular carcinoma by unknown mechanisms. Here, we show that mice with a severe defect in bile acid homeostasis due to the loss of the nuclear receptors FXR and SHP have enlarged livers, progenitor cell proliferation, and Yes-associated protein (YAP) activation and develop spontaneous liver tumorigenesis. This phenotype mirrors mice with loss of hippo kinases or overexpression of their downstream target, YAP. Bile acids act as upstream regulators of YAP via a pathway dependent on the induction of the scaffold protein IQGAP1. Patients with diverse biliary dysfunctions exhibit enhanced IQGAP1 and nuclear YAP expression. Our findings reveal an unexpected mechanism for bile acid regulation of liver growth and tumorigenesis via the Hippo pathway.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
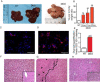

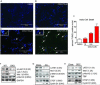
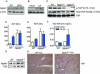

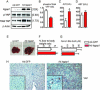
References
-
- Brown MD, Sacks DB. IQGAP1 in cellular signaling: bridging the GAP. Trends in cell biology. 2006;16:242–249. - PubMed
-
- Camargo FD, Gokhale S, Johnnidis JB, Fu D, Bell GW, Jaenisch R, Brummelkamp TR. YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Curr Biol. 2007;17:2054–2060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

