Spurious group differences due to head motion in a diffusion MRI study
- PMID: 24269273
- PMCID: PMC4029882
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.11.027
Spurious group differences due to head motion in a diffusion MRI study
Abstract
Diffusion-weighted MRI (DW-MRI) has become a popular imaging modality for probing the microstructural properties of white matter and comparing them between populations in vivo. However, the contrast in DW-MRI arises from the microscopic random motion of water molecules in brain tissues, which makes it particularly sensitive to macroscopic head motion. Although this has been known since the introduction of DW-MRI, most studies that use this modality for group comparisons do not report measures of head motion for each group and rely on registration-based correction methods that cannot eliminate the full effects of head motion on the DW-MRI contrast. In this work we use data from children with autism and typically developing children to investigate the effects of head motion on differences in anisotropy and diffusivity measures between groups. We show that group differences in head motion can induce group differences in DW-MRI measures, and that this is the case even when comparing groups that include control subjects only, where no anisotropy or diffusivity differences are expected. We also show that such effects can be more prominent in some white-matter pathways than others, and that they can be ameliorated by including motion as a nuisance regressor in the analyses. Our results demonstrate the importance of taking head motion into account in any population study where one group might exhibit more head motion than the other.
Keywords: Autism; Diffusion MRI; Motion; Tractography.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






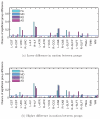



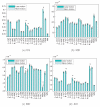
References
-
- Anderson AW, Gore JC. Analysis and correction of motion artifacts in diffusion weighted imaging. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 1994 Sep;32(3):379–387. - PubMed
-
- Andersson JLR, Skare S. A model-based method for retrospective correction of geometric distortions in diffusion-weighted EPI. NeuroImage. 2002 May;16(1):177–199. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- S10 RR019307/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR014075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052585/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG008122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AT005728/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS072652/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R00 EB008129/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB006758/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023401/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022381/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 RR021382/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K99 EB008129/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH093765/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS070963/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

