Sec-secretion and sortase-mediated anchoring of proteins in Gram-positive bacteria
- PMID: 24269844
- PMCID: PMC4031296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.11.009
Sec-secretion and sortase-mediated anchoring of proteins in Gram-positive bacteria
Abstract
Signal peptide-driven secretion of precursor proteins directs polypeptides across the plasma membrane of bacteria. Two pathways, Sec- and SRP-dependent, converge at the SecYEG translocon to thread unfolded precursor proteins across the membrane, whereas folded preproteins are routed via the Tat secretion pathway. Gram-positive bacteria lack an outer membrane and are surrounded by a rigid layer of peptidoglycan. Interactions with their environment are mediated by proteins that are retained in the cell wall, often through covalent attachment to the peptidoglycan. In this review, we describe the mechanisms for both Sec-dependent secretion and sortase-dependent assembly of proteins in the envelope of Gram-positive bacteria. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Protein trafficking and secretion in bacteria. Guest Editors: Anastassios Economou and Ross Dalbey.
Keywords: Cell wall; LPXTG; Leader peptide; Peptidoglycan; Sec; Sortase.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

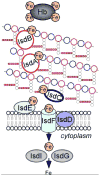

References
-
- Gram HC. Über die isolierte Färbung der Schizomyceten in Schnitt- und Trockenpräparaten. Fortschritte der Medizin. 1884;2:185–189.
-
- Bishop PJ, Neumann G. The history of the Ziehl-Neelsen stain. Tubercle. 1970;51:196–206. - PubMed
-
- Munoz E, Ghuysen JM, Heymann H. Cell walls of Streptococcus pyogenes, type 14. C polysaccharide-peptidoglycan and G polysaccharide-peptidoglycan complexes. Biochemistry. 1967;6:3659–3670. - PubMed
-
- Coley J, Archibald AR, Baddiley J. A linkage unit joining peptidoglycan to teichoic acid in Staphylococcus aureus H. FEBS Lett. 1976;61:240–242. - PubMed
-
- Schneewind O, Fowler A, Faull KF. Structure of the cell wall anchor of surface proteins in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1995;268:103–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

