Stress and CRF gate neural activation of BDNF in the mesolimbic reward pathway
- PMID: 24270188
- PMCID: PMC3984932
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3591
Stress and CRF gate neural activation of BDNF in the mesolimbic reward pathway
Abstract
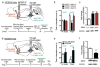
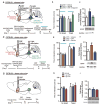
Mechanisms controlling release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the mesolimbic dopamine reward pathway remain unknown. We report that phasic optogenetic activation of this pathway increases BDNF amounts in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) of socially stressed mice but not of stress-naive mice. This stress gating of BDNF signaling is mediated by corticotrophin-releasing factor (CRF) acting in the NAc. These results unravel a stress context-detecting function of the brain's mesolimbic circuit.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 MH095425/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH092306/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007135/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 MH094405/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH087004/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F32 MH096464/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA014133/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH096678/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA022445/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH108326/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH096890/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH051399/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH092306/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

