Abscisic Acid synthesis and response
- PMID: 24273463
- PMCID: PMC3833200
- DOI: 10.1199/tab.0166
Abscisic Acid synthesis and response
Abstract
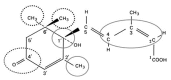
Abscisic acid (ABA) is one of the "classical" plant hormones, i.e. discovered at least 50 years ago, that regulates many aspects of plant growth and development. This chapter reviews our current understanding of ABA synthesis, metabolism, transport, and signal transduction, emphasizing knowledge gained from studies of Arabidopsis. A combination of genetic, molecular and biochemical studies has identified nearly all of the enzymes involved in ABA metabolism, almost 200 loci regulating ABA response, and thousands of genes regulated by ABA in various contexts. Some of these regulators are implicated in cross-talk with other developmental, environmental or hormonal signals. Specific details of the ABA signaling mechanisms vary among tissues or developmental stages; these are discussed in the context of ABA effects on seed maturation, germination, seedling growth, vegetative stress responses, stomatal regulation, pathogen response, flowering, and senescence.
Figures

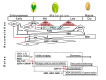



References
-
- Acevedo-Hernández G.J., León P., Herrera-Estrella L.R. Sugar and ABA responsiveness of a minimal RBCS light-responsive unit is mediated by direct binding of ABI4. Plant J. 2005;43:506–519. - PubMed
-
- Ache P., Becker D., Ivashikina N., Dietrich P., Roelfsema M.R.G., Hedrich R. GORK, a delayed outward rectifier expressed in guard cells of Arabidopsis thaliana, is a K+-selective, K+-sensing ion channel. FEBS Letters. 2000;486:93–98. - PubMed
-
- Alexandersson E., Fraysse L., Sjovall-Larsen S., Gustavsson S., Fellert M., Karlsson M., Johanson U., Kjellbom P. Whole gene family expression and drought stress regulation of aquaporins. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005;59:469–484. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
