Dendritic cell derived cytokines in human natural killer cell differentiation and activation
- PMID: 24273539
- PMCID: PMC3822368
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00365
Dendritic cell derived cytokines in human natural killer cell differentiation and activation
Abstract
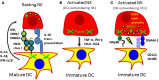
Dendritic cells (DCs) and natural killer (NK) cells shape each other's functions early during immune responses. DCs activate NK cells and NK cells can mature or kill DCs. In this review we will discuss which DC and NK cell subsets are mainly affected by this interaction, where these encounters might take place and which signals are exchanged. Finally, we will point out what the clinical benefit of understanding this interaction might be and how it changed our view on NK cells as innate lymphocytes.
Keywords: DNAM-1; IFN-alpha; IL-12; IL-15; IL-18; NKp30; immunological synapse.
Figures
References
-
- Herberman RB, Nunn ME, Lavrin DH. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic acid allogeneic tumors. I. Distribution of reactivity and specificity. Int J Cancer (1975) 16:216–29 - PubMed
-
- Trinchieri G, Santoli D. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by interferon and antagonistic inhibition of susceptibility of target cells to lysis. J Exp Med (1978) 147:1314–3310.1084/jem.147.5.1299 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

