The efficacy and safety of a proposed herbal moisturising cream for dry skin and itch relief: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial--study protocol
- PMID: 24274317
- PMCID: PMC4222493
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-330
The efficacy and safety of a proposed herbal moisturising cream for dry skin and itch relief: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial--study protocol
Abstract
Background: Moisturisers prevent and treat dry skin. They can also protect sensitive skin, improve skin tone and texture, and mask imperfections. Herbal medicines or their extracts have been available as topical formulations and cosmetics. Arctium lappa L. (Asteraceae) has been used to treat inflammatory disorders and various skin problems. It could be a candidate herbal medicine for treating dry skin condition.This study aims to establish the efficacy and safety of a proposed herbal moisturising cream containing Arctium lappa L. seed extract, which has been approved by the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety for use in cosmetics.
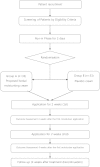
Methods/designs: This study is a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study with two parallel groups (proposed herbal moisturising cream vs. placebo cream). We will recruit 66 healthy male and female participants, aged 20 to 65 years, who have been diagnosed with dry skin conditions. Participants will be randomly allocated to receive either the proposed herbal moisturising cream or a placebo cream for four weeks. Each participant will be examined for signs and symptoms before and after using the cream. Skin hydration, sebum (oily secretion) levels and transepidermal water loss (TEWL; constitutive loss of water from the skin surface) will be assessed. Participants will also be asked to fill out a health-related quality of life questionnaire. Safety will be assessed using blood tests, urine analysis, a pregnancy test, and the assessment of vital signs.
Discussion: This trial will utilise high-quality methodologies in accordance with both consolidated standards for reporting trials guidelines and the guidelines for clinical trials of cosmetics products that are aimed at expressions and advertisement approval in Korea. It will evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of a proposed herbal moisturising cream containing Arctium lappa L. seed extract to treat dry skin conditions and provide itch relief. Moreover, we will also employ health-related quality of life questionnaires to assess changes in the quality of life. The results of this study will be used to present the evidence needed to request advertising/display allowances, in compliance with the recently amended Cosmetics Act for advertisement in Korea.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN46216631.
Similar articles
-
Hwangryunhaedoktang in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-centre trial--study protocol.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011 Aug 23;11:68. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-11-68. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011. PMID: 21861896 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Woad extract containing cream improves significantly dry, irritated, and pruritic skin.Dermatol Ther. 2019 Jul;32(4):e12939. doi: 10.1111/dth.12939. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Dermatol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30990240
-
Hygiene and emollient interventions for maintaining skin integrity in older people in hospital and residential care settings.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 23;1(1):CD011377. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011377.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32006460 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Pruritic Efficacy of Itch Relief Lotion and Cream in Patients With Atopic History: Comparison With Hydrocortisone Cream.J Drugs Dermatol. 2017 Mar 1;16(3):243-247. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28301620 Clinical Trial.
-
Patient acceptability, efficacy, and skin biophysiology of a cream and cleanser containing lipid complex with shea butter extract versus a ceramide product for eczema.Hong Kong Med J. 2015 Oct;21(5):417-25. doi: 10.12809/hkmj144472. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Hong Kong Med J. 2015. PMID: 26314567 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-world effectiveness and tolerability of Zelesse cream® for treating vulvovaginitis in adult women: an observational, prospective study.J Int Med Res. 2021 May;49(5):3000605211013226. doi: 10.1177/03000605211013226. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33983051 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Use of Compressive Stockings Impregnated With Hesperetin-Based Nanocapsules in the Healing of Venous Ulcers: A Case Report.Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2019 Jul 18;12:1179547619858977. doi: 10.1177/1179547619858977. eCollection 2019. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31360076 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of the anti-inflammatory effects, pharmacokinetic properties and clinical efficacies of arctigenin and arctiin from Arctium lappa L.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 May;39(5):787-801. doi: 10.1038/aps.2018.32. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 29698388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production and characterization of cosmetic nanoemulsions containing Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) mill extract as moisturizing agent.Molecules. 2015 Feb 2;20(2):2492-509. doi: 10.3390/molecules20022492. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25648593 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials