Characterization of early autophagy signaling by quantitative phosphoproteomics
- PMID: 24275748
- PMCID: PMC5396084
- DOI: 10.4161/auto.26864
Characterization of early autophagy signaling by quantitative phosphoproteomics
Abstract
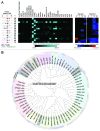
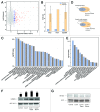
Under conditions of nutrient shortage autophagy is the primary cellular mechanism ensuring availability of substrates for continuous biosynthesis. Subjecting cells to starvation or rapamycin efficiently induces autophagy by inhibiting the MTOR signaling pathway triggering increased autophagic flux. To elucidate the regulation of early signaling events upon autophagy induction, we applied quantitative phosphoproteomics characterizing the temporal phosphorylation dynamics after starvation and rapamycin treatment. We obtained a comprehensive atlas of phosphorylation kinetics within the first 30 min upon induction of autophagy with both treatments affecting widely different cellular processes. The identification of dynamic phosphorylation already after 2 min demonstrates that the earliest events in autophagy signaling occur rapidly after induction. The data was subjected to extensive bioinformatics analysis revealing regulated phosphorylation sites on proteins involved in a wide range of cellular processes and an impact of the treatments on the kinome. To approach the potential function of the identified phosphorylation sites we performed a screen for MAP1LC3-interacting proteins and identified a group of binding partners exhibiting dynamic phosphorylation patterns. The data presented here provide a valuable resource on phosphorylation events underlying early autophagy induction.
Keywords: autophagy; bioinformatics; mass spectrometry; phosphoproteomics; phosphorylation; proteomics; signal transduction.
Figures
References
-
- Rabinowitz JD, White E. . Autophagy and metabolism. Science 2010; 330:1344 - 8; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1193497; PMID: 21127245 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Duve C, Wattiaux R. . Functions of lysosomes. Annu Rev Physiol 1966; 28:435 - 92; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ph.28.030166.002251; PMID: 5322983 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Klionsky DJ. . Autophagy: from phenomenology to molecular understanding in less than a decade. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8:931 - 7; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm2245; PMID: 17712358 - DOI - PubMed
-
- He C, Klionsky DJ. . Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet 2009; 43:67 - 93; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-102808-114910; PMID: 19653858 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Johansen T, Lamark T. . Selective autophagy mediated by autophagic adapter proteins. Autophagy 2011; 7:279 - 96; http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/auto.7.3.14487; PMID: 21189453 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
