Mapping three-dimensional temperature in microfluidic chip
- PMID: 24276475
- PMCID: PMC3839638
- DOI: 10.1038/srep03321
Mapping three-dimensional temperature in microfluidic chip
Abstract
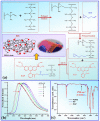
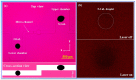
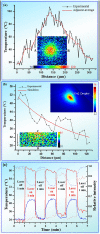
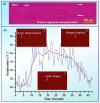
Three-dimensional (3D) temperature mapping method with high spatial resolution and acquisition rate is of vital importance in evaluating thermal processes in micro-environment. We have synthesized a new temperature-sensitive functional material (Rhodamine B functionalized Polydimethylsiloxane). By performing optical sectioning of this material, we established an advanced method for visualizing the micro-scale 3D thermal distribution inside microfluidic chip with down to 10 ms temporal resolution and 2 ~ 6 °C temperature resolution depending the capture parameters. This method is successfully applied to monitor the local temperature variation throughout micro-droplet heat transfer process and further reveal exothermic nanoliter droplet reactions to be unique and milder than bench-top experiment.
Figures
References
-
- Brites C. D. S. et al. Thermometry at the nanoscale. Nanoscale 4, 4799–4829 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Wu J., Zhang M., Li X. & Wen W. Multiple and high-throughput droplet reactions via combination of microsampling technique and microfluidic chip. Anal. Chem. 84, 9689–9693 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Tsuji K. & Mueller S. C. Chemical Reaction Evolving on a Droplet. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3, 977–980 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

