UKALLXII/ECOG2993: addition of imatinib to a standard treatment regimen enhances long-term outcomes in Philadelphia positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 24277073
- PMCID: PMC3916877
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-09-529008
UKALLXII/ECOG2993: addition of imatinib to a standard treatment regimen enhances long-term outcomes in Philadelphia positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
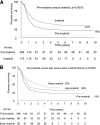
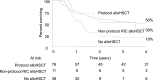
The Philadelphia chromosome positive arm of the UKALLXII/ECOG2993 study for adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) enrolled 266 patients between 1993 and 2003 (pre-imatinib cohort). In 2003 imatinib was introduced as a single-agent course following induction (N = 86, late imatinib). In 2005 imatinib was added to the second phase of induction (N = 89, early imatinib). The complete remission (CR) rate was 92% in the imatinib cohort vs 82% in the preimatinib cohort (P = .004). At 4 years, the overall survival (OS) of all patients in the imatinib cohort was 38% vs 22% in the preimatinib cohort (P = .003). The magnitude of the difference between the preimatinib and imatinib cohorts in event-free survival (EFS), OS, and relapse-free survival (RFS) seen in univariate analysis was even greater in the multivariate analysis. In the preimatinib cohort, 31% of those starting treatment achieved hematopoietic stem cell transplant (alloHSCT) compared with 46% in the imatinib cohort. A Cox multivariate analysis taking alloHSCT into account showed a modest additional benefit to imatinib (hazard ratio for EFS = 0.64, 95% confidence interval 0.44-0.93, P = .02), but no significant benefit for OS and RFS. Adding imatinib to standard therapy improves CR rate and long-term OS for adults with ALL. A proportion of the OS benefit derives from the fact that imatinib facilitates alloHSCT. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT00002514.
Figures


Comment in
-
Ph+ ALL: imatinib grows older with patients.Blood. 2014 Feb 6;123(6):801-3. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-12-542423. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24505064 No abstract available.
References
-
- Moorman AV, Harrison CJ, Buck GA, et al. Adult Leukaemia Working Party, Medical Research Council/National Cancer Research Institute. Karyotype is an independent prognostic factor in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): analysis of cytogenetic data from patients treated on the Medical Research Council (MRC) UKALLXII/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) 2993 trial. Blood. 2007;109(8):3189–3197. - PubMed
-
- Fielding AK. How I treat Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2010;116(18):3409–3417. - PubMed
-
- de Labarthe A, Rousselot P, Huguet-Rigal F, et al. Group for Research on Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (GRAALL) Imatinib combined with induction or consolidation chemotherapy in patients with de novo Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of the GRAAPH-2003 study. Blood. 2007;109(4):1408–1413. - PubMed
-
- Thomas DA, Faderl S, Cortes J, et al. Treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphocytic leukemia with hyper-CVAD and imatinib mesylate. Blood. 2004;103(12):4396–4407. - PubMed
-
- Towatari M, Yanada M, Usui N, et al. Japan Adult Leukemia Study Group. Combination of intensive chemotherapy and imatinib can rapidly induce high-quality complete remission for a majority of patients with newly diagnosed BCR-ABL-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2004;104(12):3507–3512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 CA013650/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA13650/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA017145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U10 CA014548/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA15488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA015488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14548/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037403/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA17145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA114737/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

