Hepatitis C therapy with interferon-α and ribavirin reduces CD4 T-cell-associated HIV-1 DNA in HIV-1/hepatitis C virus-coinfected patients
- PMID: 24277743
- PMCID: PMC3982848
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jit628
Hepatitis C therapy with interferon-α and ribavirin reduces CD4 T-cell-associated HIV-1 DNA in HIV-1/hepatitis C virus-coinfected patients
Abstract
Combined treatment with interferon alpha (IFN-α) and ribavirin (RBV) can effectively cure HCV infection in a significant proportion of patients, but effects of this regimen on cellular reservoirs for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) are unknown. Here, we show that treatment with IFN-α/RBV led to a moderate but significant and sustained decline of HIV-1 DNA in CD4 T cells from HIV-1/hepatitis C virus-coinfected patients receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy (n = 12). However, in vitro experiments failed to demonstrate an effect of pharmacological doses of IFN-α on HIV-1 reactivation. Together, these data suggest that treatment with IFN-α/RBV can moderately reduce the reservoir of HIV-1-infected CD4 T cells that persists despite suppressive antiretroviral therapy.
Keywords: HIV-1 reservoir; HIV-1/HCV coinfection; interferon-α; ribavirin.
Figures
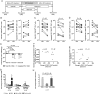
 ; Patient 2:
; Patient 2:  ; Patient 3:
; Patient 3:  ; Patient 4:
; Patient 4:  ; Patient 5:
; Patient 5:  ; Patient 6:
; Patient 6:  ; Patient 7:
; Patient 7:  ; Patient 8:
; Patient 8:  ; Patient 9:
; Patient 9:  ; Patient 10:
; Patient 10:  ; Patient 11:
; Patient 11:  ; Patient 12:
; Patient 12:  . E, Fold change of HIV-1 DNA in indicated time intervals. Data reflect median and range. F, Inverse association between maximum CD4 T-cell changes during HCV therapy and corresponding absolute and relative changes in CD4 T-cell–associated integrated HIV-1 DNA. Spearman correlation coefficients are shown. G, Analysis of HIV-1 RNA and total or integrated HIV-1 DNA in primary CD4 T cells from highly active antiretroviral therapy–treated patients after in vitro exposure to IFN-α, IFN-α + RBV, or panobinostat. *P = .06 in comparison to untreated control. H, IRF7 mRNA expression in CD4 T cells after in vitro exposure to IFN-α, RBV or IFN-α + RBV.
. E, Fold change of HIV-1 DNA in indicated time intervals. Data reflect median and range. F, Inverse association between maximum CD4 T-cell changes during HCV therapy and corresponding absolute and relative changes in CD4 T-cell–associated integrated HIV-1 DNA. Spearman correlation coefficients are shown. G, Analysis of HIV-1 RNA and total or integrated HIV-1 DNA in primary CD4 T cells from highly active antiretroviral therapy–treated patients after in vitro exposure to IFN-α, IFN-α + RBV, or panobinostat. *P = .06 in comparison to untreated control. H, IRF7 mRNA expression in CD4 T cells after in vitro exposure to IFN-α, RBV or IFN-α + RBV.References
-
- Hoofnagle JH, Seeff LB. Peginterferon and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2444–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

