Synthesis and delivery of short, noncoding RNA by B lymphocytes
- PMID: 24277816
- PMCID: PMC3864290
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1311145110
Synthesis and delivery of short, noncoding RNA by B lymphocytes
Abstract
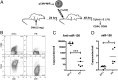
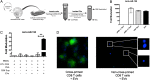
Evolutionarily conserved short (20-30 nucleotides) noncoding RNAs (microRNAs) are powerful regulators of gene expression in a variety of physiological and pathological processes. As such, means to efficiently modulate microRNA function constitute an important therapeutic opportunity. Here we demonstrate that primary B lymphocytes can be genetically programmed with nonviral plasmid DNA for the biogenesis and delivery of antisense sequences (anti-microRNA) against microRNA-150 (miR-150). Within 18 h of transfection with an anti-miR-150 construct, primary B lymphocytes secrete ∼3,000 copies of anti-miR-150 molecules per cell. Anti-miR-150 molecules released by B lymphocytes were internalized by CD8 T lymphocytes during cross-priming in vitro and in vivo, resulting in marked down-regulation of endogenous miR-150. However, such internalization was not observed in the absence of cross-priming. These results suggest that shuttling anti-miR-150 molecules from B lymphocytes to T cells requires the activation of receiver T cells via the antigen receptor. Finally, anti-miR-150 synthesized in B cells were secreted both as free and extracellular vesicle-associated fractions, but only extracellular vesicle-associated anti-miR-150 were apparently taken up by CD8 T cells. Collectively, these data indicate that primary B lymphocytes represent an efficient platform for the synthesis and delivery of short, noncoding RNA, paving the way for an approach to immunogenomic therapies.
Keywords: immunotherapy; microvesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–297. - PubMed
-
- Thomas M, Lieberman J, Lal A. Desperately seeking microRNA targets. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010;17(10):1169–1174. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431(7006):350–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

